In a previous article, we have shared an overview of blockchain technology’s intricate procedures, multiple transactions, and diverse stakeholders. In this detailed article, we will decode a detailed analysis on blockchain technology advantages, types, advantages, market potential and applications.
As the real estate sector continues its evolution, there's a huge demand for technological solutions, driven by a quest for heightened efficiency and security. Among these technological advancements, blockchain has emerged as a transformative force, offering a paradigm shift in how real estate transactions are conducted. By using a decentralized and immutable ledger system, blockchain enhances transparency in property transactions, reducing the risk of fraud and ensuring trust among stakeholders. This technology streamlines processes such as title transfers and smart contracts, ultimately revolutionizing how real estate transactions are conducted and recorded. The growing integration of blockchain signifies a shift towards a more robust, secure, and digitally-driven future for the real estate sector.
What is Blockchain technology?
Blockchain technology is a decentralized and distributed ledger system that securely records and verifies transactions. It operates as a chain of blocks, where each block contains a list of transactions linked together through cryptographic hashes. In the context of real estate, blockchain can be used to create transparent and tamper-resistant records of property transactions, ownership, and other relevant information. This technology enhances trust among parties, reduces the risk of fraud, and streamlines processes such as property transfers and smart contracts, ultimately bringing increased efficiency and security to the real estate industry.
Advantages of Blockchain Technology in Real Estate
1. Decentralization: In the real estate sector, decentralization through blockchain means that property transactions and ownership records are maintained across a distributed network of computers rather than a single, central authority. This setup minimizes the risk of data manipulation, errors, and fraud that can occur in centralized systems. By eliminating intermediaries such as government registries or central databases, real estate transactions become more secure and transparent. All participants, including buyers, sellers, and regulators, can access and verify information in real-time, fostering trust and reducing bureaucratic inefficiencies.
2. Transparency: Blockchain’s inherent transparency offers a significant advantage for real estate transactions. All transaction records are publicly accessible and immutable, providing a clear and verifiable history of property ownership. This transparency ensures that all parties involved in a transaction can trust the data they are viewing. For example, potential buyers can confirm the legitimacy of the property title, check for any existing liens, and verify the property's transaction history. This reduces the likelihood of fraud and disputes, streamlining the due diligence process and increasing overall market confidence.
3. Security: Security is paramount in real estate transactions due to the high value of the assets involved. Blockchain technology enhances security by using cryptographic techniques to protect transaction data and property records. Each transaction is linked to the previous one, creating a secure chain that is difficult to alter without detection. This makes property titles, contracts, and personal data of buyers and sellers highly secure from hacking and unauthorized access. The decentralized nature of blockchain also ensures that there is no single point of failure, further protecting against data breaches and fraud.
4. Immutability: The immutability of blockchain records is particularly beneficial for real estate. Once a transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted. This permanence provides a reliable and tamper-proof record of property ownership and transaction history. It ensures that historical data remains accurate and trustworthy, which is crucial for resolving disputes and verifying titles. This immutability also simplifies the process of due diligence for potential buyers and investors, as they can be confident in the accuracy of the information provided.
5. Efficiency: Blockchain technology can significantly increase the efficiency of real estate transactions by automating many processes. Smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code, can handle various aspects of the transaction, such as verifying ownership, conducting due diligence, and executing the transfer of property. This automation reduces the need for intermediaries like brokers, lawyers, and notaries, cutting down on the time and cost associated with traditional real estate transactions. For instance, a property sale that might traditionally take weeks or even months can be completed in just a few days using blockchain technology.
6. Traceability: Blockchain provides an immutable and detailed record of all transactions, making it easier to trace the ownership history and legal status of a property. This traceability is crucial for identifying and resolving any issues that may arise during a property transaction. For example, it can help verify that a property is free from liens or other encumbrances before a sale. This capability simplifies the due diligence process for buyers and increases their confidence in the transaction. Additionally, traceability can help regulators and authorities monitor real estate transactions to ensure compliance with laws and regulations.
7. Cost Reduction: Blockchain technology can significantly reduce the costs associated with real estate transactions by eliminating intermediaries and automating processes. Traditional transactions often involve multiple parties, including brokers, lawyers, notaries, and escrow services, each of which adds to the overall cost. By using blockchain, many of these roles can be streamlined or even eliminated, reducing transaction fees and administrative costs. Additionally, the reduction in paperwork and the need for physical document storage can further lower operational expenses, making real estate transactions more affordable for all parties involved.
8. Enhanced Privacy: While blockchain is transparent, it also offers enhanced privacy features. Property transactions and ownership details can be recorded using pseudonyms or encrypted identities, ensuring that personal information remains confidential. This balance between transparency and privacy is particularly important in high-value property deals, where buyers and sellers may wish to keep their identities and transaction details private. Enhanced privacy also protects sensitive information from unauthorized access and potential misuse, providing an additional layer of security for all parties involved.
9. Innovation and New Business Models: Blockchain enables innovative business models in the real estate sector, such as fractional ownership and tokenization of property assets. Fractional ownership allows multiple investors to own a share of a property, making real estate investment more accessible to a broader audience. Tokenization involves creating digital tokens that represent real-world properties, which can be traded on blockchain platforms. These innovations increase liquidity in the real estate market and open up new investment opportunities, particularly for smaller investors who may not have the capital to purchase entire properties.
10. Accessibility: Blockchain technology can make real estate markets more accessible by simplifying the process of buying, selling, and investing in property. This increased accessibility is particularly beneficial for individuals in regions with limited banking infrastructure or high barriers to entry. By providing a decentralized platform for real estate transactions, blockchain can democratize property investment, allowing more people to participate in the market. This increased accessibility can drive economic growth and development, particularly in underserved areas, by enabling a more diverse group of investors to participate in real estate transactions.
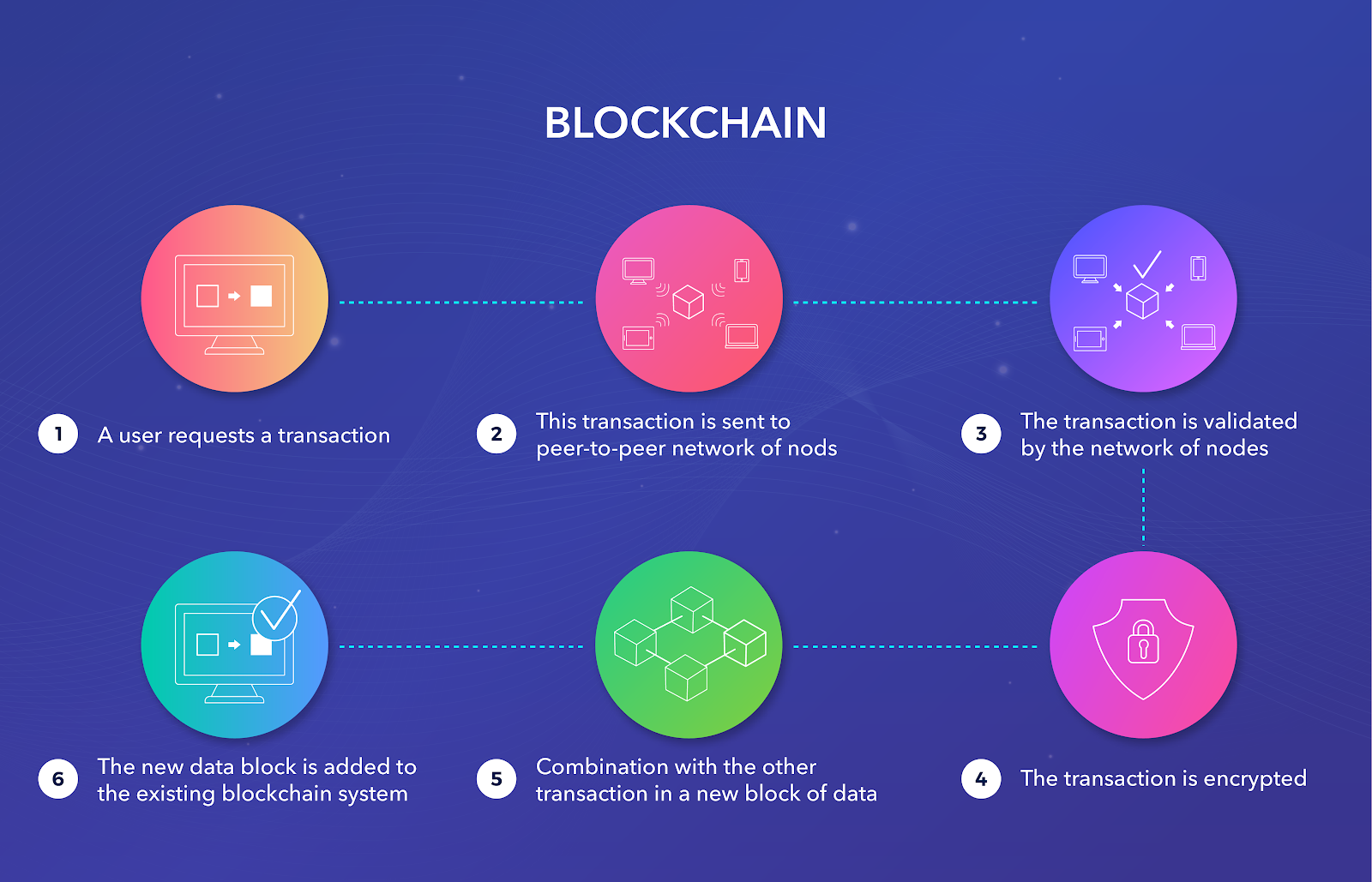
Different types of Blockchain Technology?
1. Tokenization Platforms: In the realm of real estate, tokenization platforms leverage blockchain technology to represent property assets as digital tokens. This process allows for the fractional ownership of real estate, enabling investors to own a portion of a property. This innovation enhances liquidity in the market by making real estate investments more accessible to a broader range of individuals. Tokenization platforms streamline the buying and selling of these digital assets, offering a novel approach to real estate investment and wealth management.
2. Smart Contracts: Blockchain-based smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. In the context of real estate, smart contracts automate and enforce contractual obligations without the need for intermediaries. These contracts can facilitate property transactions, rental agreements, and other real estate processes, reducing the risk of disputes and enhancing overall efficiency. By executing predefined conditions automatically, smart contracts bring transparency and trust to real estate transactions.
3. Property Registries: Real estate transactions often rely on accurate and tamper-proof records of property ownership. Blockchain-based property registries provide a decentralized and secure ledger for recording and verifying these transactions. This technology ensures transparency in land titles, minimizing the risk of fraud or errors associated with traditional paper-based systems. Property registries on the blockchain enhance the reliability of land ownership records, improving the overall integrity of real estate markets.
4. Decentralized Identity Verification: Blockchain contributes to secure and decentralized identity verification processes in real estate. By using cryptographic techniques, individuals can have their identities verified without relying on a centralized authority. This is particularly beneficial for tenant screenings, where a reliable and tamper-resistant identity verification system can streamline rental processes and enhance security for both landlords and tenants.
5. Supply Chain Tracking: Blockchain technology is applied to track the supply chain of construction materials in real estate development. By recording the origin, movement, and processing of materials on a transparent and immutable ledger, stakeholders can ensure the quality and authenticity of construction inputs. This application enhances accountability, reduces the risk of substandard materials, and contributes to sustainable and efficient real estate development practices.
6. Data Security and Privacy: Blockchain addresses data security concerns in real estate by providing a decentralized and immutable ledger. This ensures that critical information, such as property records, transactions, and sensitive personal data, remains secure from tampering and unauthorized access. Implementing blockchain in real estate transactions enhances privacy and reduces the risk of fraudulent activities, contributing to a more secure and reliable ecosystem for both property owners and stakeholders involved in real estate transactions.
7. Cross-Border Transactions: Blockchain facilitates cross-border real estate transactions by overcoming traditional challenges associated with currency exchanges, processing times, and complex documentation. Through the use of digital currencies and smart contracts, blockchain streamlines the transfer of funds and automates various aspects of cross-border transactions. This results in faster and more cost-effective real estate dealings across international borders, opening up new opportunities for global property investments.
8. Energy Efficiency and Sustainability: Blockchain technology is employed to monitor and incentivize sustainable practices in real estate development. Through the use of smart contracts and tokenization, stakeholders can track and reward energy-efficient buildings, green construction materials, and eco-friendly practices. This promotes sustainability in the real estate industry by encouraging environmentally conscious choices and providing a transparent way to showcase and verify the adherence to green standards in construction and property management.
Global Market Potential of Blockchain Technology
As per, Precedence Research report, The global blockchain technology market size was estimated at USD 4.8 billion in 2022 and is expected to be around USD 2,334.46 billion by 2032, poised to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 85.7% during the forecast period 2023 to 2032.
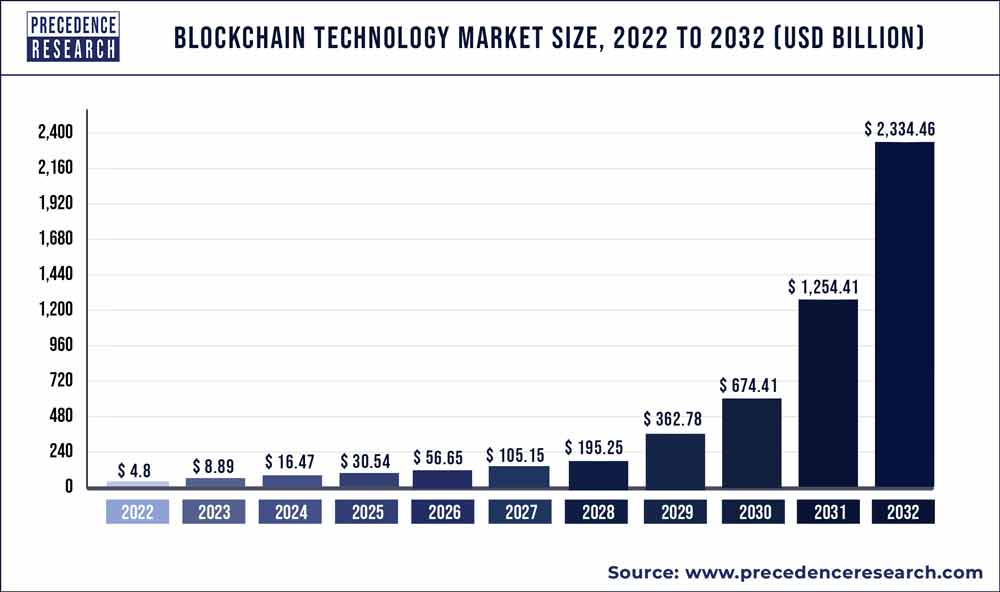
The growing demand for e-identity has driven the expansion of Blockchain technology. The platforms based on blockchain technology have diverse applications in countries with weak identification processes and in unregulated countries. At the national level, the adoption of market demand-based identity platforms of Blockchain technology has been carried out by many governments in order to promote secure transactions in the public and private sectors. Various governments have been using blockchain technology with their e-citizenship programs over the past few years.
In addition, the growing capitalization of market-linked cryptocurrencies has promoted the risk of capital investments made by different countries. According to the size of the Blockchain technology market, cryptocurrency has marked innovation in different payment contexts. Furthermore, compared to other types of payment, these currencies offer lower transaction fees. Furthermore, because transaction fees are expensive, cryptocurrencies are attracting businesses and individuals to use cross-border payment methods. Also, due to the decentralized ownership of these cryptocurrencies, cross-border regulators cannot impose any kind of restrictions on these transactions. Therefore, low transaction fees and many other factors are beneficial to Blockchain technology market revenue as well as cryptocurrency capitalization, which motivates venture capitalists to invest in Blockchain technology market share.
Asia Pacific Market Potential of Blockchain Technology
As per maximizemarketresearch report, The Asia Pacific Blockchain Market value is projected to reach US$ 10.11 Bn. at the end of the forecast period and it is expected to grow at the CAGR of 30.2%. In terms of geography, Asia Pacific Blockchain Market is segmented into China, India, Japan, South Korea, Australia, and others. Asia Pacific accounting for highest CAGR during the forecast period. The blockchain market is growing rapidly in the Asia Pacific region. For example, China is increasingly using blockchain technology for economic development.
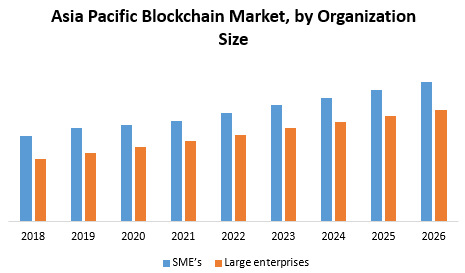
Reduced total cost of ownership, rising cryptocurrencies market cap and initial coin offerings are few major drivers that have positively driven overall growth of the market. In addition to this, increasing demand for simplified business processes, transparency, immutability, faster transactions with reduced costs and increasing use of blockchain as a service are also responsible for the growth of the Asia Pacific Blockchain Market. The increasing use of blockchain across smart contracts, document management and digital identities in the media industry are some main areas that are propelling the overall growth of the blockchain market. Highly cost-effective and time-efficiency form two key features for blockchain application as well in both large and small enterprises.
Applications of Blockchain Technology by the Indian Government
Government of India has been taking a keen interest in blockchain technology and its application to the public domain, as is evident from the release of the “National Strategy on Blockchain” by MeitY in December 2021, which elucidated its vision to adopt blockchain in various sectors like healthcare, agriculture, finance, voting and e-governance, while laying the groundwork for establishing a “National Blockchain Framework,” under which it will work towards building a national-level infrastructure for blockchain. It hopes to enable “Made in India” blockchain technology for global use by 2027 while achieving convergence across blockchain, Internet of Things, cloud and Artificial Intelligence, collectively called the “BICA Stack.” The government is currently in the process of deploying blockchain technology for land registration, issuing digital certificates and customs duty payment.
Local and state governments have embraced the adoption of blockchain technology as well, and are in the process of incorporating it into their governance structures. Almost half the states in the country are currently working on blockchain-related initiatives.
One of the most remarkable cases is the adoption of NFTs for land mutation by the New Town Kolkata Development Authority in West Bengal. Covering an area of 27,000 acres, a total of 50,000 NFTs have been implemented, representing one million property records. The NFTs provide proof of land ownership and all documents embedded with them are free from tampering, thereby making the land mutation process transparent while eliminating the need for manual paperwork and record-keeping. The state of Andhra Pradesh has also launched a pilot project to use blockchain to record and track land ownership records. The state of Maharashtra is also exploring the use of blockchain for property registration.
Despite the potential benefits, there are still some challenges that need to be addressed before blockchain can be widely adopted in the Indian real estate industry. One of the major challenges is the lack of standardization in the technology, which can make it difficult for different systems to communicate with each other. Additionally, there is a need for more education and awareness about blockchain among real estate professionals and the general public.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology stands at the forefront of innovation, offering transformative potential across various industries. Its decentralized and tamper-resistant nature has the power to redefine traditional processes, enhance security, and foster transparency. In the realm of real estate, blockchain promises streamlined transactions, reduced paperwork, and a more accessible investment landscape through tokenization.
While the technology holds immense promise, challenges such as regulatory adaptations, standardization, and industry-wide collaboration need to be addressed for widespread adoption. As these hurdles are overcome, the impact of blockchain on sectors like real estate in India could be profound, ushering in an era of increased efficiency, trust, and accessibility. The journey toward blockchain integration requires not only technological advancements but also concerted efforts from policymakers, businesses, and stakeholders to unlock its full potential and shape a more resilient and transparent future.
Cover image-fibree.org









.png)