In today's world, sustainability has become an important consideration in construction, with the escalating urgency for environmentally conscious practices. This necessitates an increased focus on green building practices and products. Recognizing the necessity, the Indian Green Building Council (IGBC) is encouraging the adoption of sustainable and energy-efficient practices within the construction industry. In the following article, we will delve into the functions, initiatives, and the pivotal role played by the body in upholding sustainability in India.
What is IGBC?
IGBC is India's green building certification body, headquartered in Hyderabad, a part of the Confederation of Indian Industry. The IGBC promotes sustainable and environmentally friendly practices in the construction industry, encouraging the development of green buildings in India. Its main role is to promote sustainable and green building practices in India by developing and administering green building rating systems, providing certifications, and raising awareness about environmentally responsible construction and maintenance of buildings.
Committee members of the council comprise stakeholders from the construction industry, including architects, developers, product manufacturers, corporations, government bodies, academia, and nodal agencies. They actively participate in council activities through local chapters. The council collaborates closely with several State Governments, the Central Government, the World Green Building Council, and bilateral/multilateral agencies to promote green building concepts in the country.
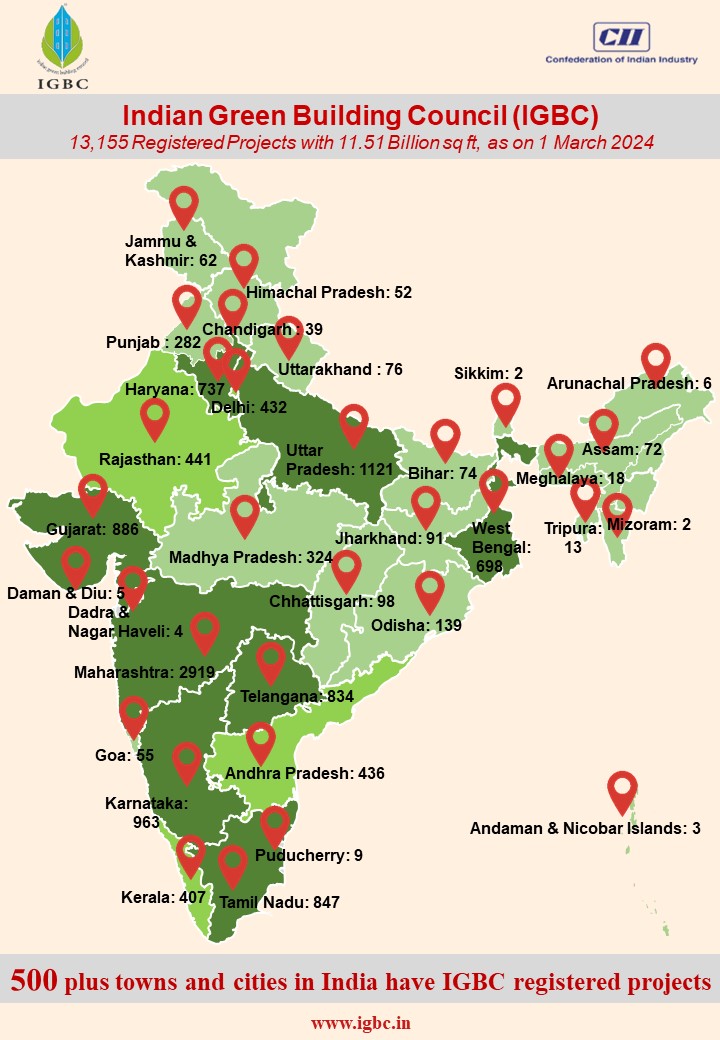
Milestones Achieved by IGBC;
- 13,115 projects with a green footprint of over 11.51 Billion Sq.Ft. as on March 1, 2024
- 3,653 projects are certified & fully operational
- 8,50,844 Acres of Large developments
- Green building ratings that encompass all project typologies, including residential, commercial, industrial, healthcare, etc.
Energy Efficiency, CO2 emission control and water saving by IGBC over the years
- 23.5 Billion of Energy savings per million sq ft per annum
- 72.3 Billion litres of Water savings per million sq ft per annum
- Reduced CO2 emissions by 19.2 Million tonnes per million sq ft per annum
- Diverted 2.5 Million tonnes of construction waste from landfill every year
Key Roles of IGBC:
Green Building Certification: The IGBC provides green building certification through various rating systems, incentivizing the construction of environmentally sustainable buildings. These certifications are designed to encourage the adoption of sustainable practices in construction and building operations. The process involves a comprehensive evaluation of the building based on several criteria, such as energy efficiency, water conservation, and the use of sustainable materials. Buildings that meet the specified standards are awarded different levels of certification, namely Certified, Silver, Gold, and Platinum. Each level represents a higher commitment to sustainability, helping to promote a culture of green building practices across the industry.
Workshops, Training Programs, and Awareness Campaigns: To further its mission of promoting sustainable building practices, IGBC conducts numerous workshops, training programs, and awareness campaigns. These activities aim to educate and train professionals, stakeholders, and the public about the importance and implementation of green building practices. By providing up-to-date knowledge and practical skills, IGBC ensures that a wide range of participants—from architects and engineers to policymakers and students—are well-equipped to contribute to the sustainable development of buildings. This continuous education fosters a community that values and understands the benefits of green construction.
Research and Development: IGBC engages in extensive research and development to innovate and develop new technologies that support sustainable building practices. Through collaborations with academic institutions, industry partners, and research organizations, IGBC focuses on creating advanced materials, energy-efficient systems, and construction methods that reduce the environmental impact of buildings. This commitment to research ensures that the industry can continually evolve and improve, incorporating the latest advancements in sustainability into mainstream building practices.
Policy Advocacy: One of IGBC's crucial roles is to promote and influence policies and regulations that support green building practices at both national and regional levels. By working closely with government bodies, IGBC helps formulate policies that incentivize sustainable construction. These incentives can include tax benefits, fast-track approval processes for green projects, and subsidies. Such policy support is vital for encouraging widespread adoption of sustainable practices in the construction industry, leading to long-term environmental benefits and economic savings.
Knowledge Sharing: IGBC facilitates opportunities for professionals in the construction industry to share knowledge and best practices. This is achieved through organizing conferences, forums, and networking events where experts can exchange their experiences, innovations, and success stories. By creating a platform for dialogue and collaboration, IGBC helps to disseminate valuable insights and foster a community committed to sustainable building practices. This knowledge sharing is essential for driving continuous improvement and innovation within the industry.

IGBC Rating Systems:
IGBC's green building ratings provide a comprehensive framework for evaluating and reducing the environmental impact of buildings. These ratings integrate life cycle considerations and are applicable across all climatic zones in India. The voluntary, market-driven approach of these ratings is gaining both national and global significance, reflecting a growing commitment to sustainability in the construction industry. The ratings cover a range of criteria, including site selection, water efficiency, energy usage, materials and resources, indoor environmental quality, innovation in design, and regional priority.
Site Selection:
In the IGBC rating system, site selection is a critical factor. This criterion evaluates the location of the building based on its proximity to public transportation, its impact on local ecosystems, and the promotion of sustainable land use. By encouraging the use of previously developed land and reducing urban sprawl, the rating system helps to minimize the environmental footprint of new constructions and promotes more sustainable urban planning practices.
Water Efficiency:
Water conservation is a major focus in the IGBC rating system. This criterion includes measures such as rainwater harvesting, the use of water-efficient fixtures, and the recycling or treatment of wastewater. By implementing these practices, buildings can significantly reduce their water consumption, alleviate pressure on local water resources, and promote sustainable water management practices that are crucial in water-scarce regions.
Energy Usage:
Energy efficiency is another key emphasis in the IGBC rating system. Buildings are evaluated based on their use of energy-efficient technologies, such as LED lighting, high-performance HVAC systems, and renewable energy sources like solar power. By optimizing energy use, buildings can lower their energy consumption, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and decrease their overall carbon footprint, contributing to broader climate change mitigation efforts.
Materials and Resources:
The materials and resources criterion in the IGBC rating system assesses the use of sustainable building materials, resource-efficient construction practices, and waste reduction strategies. By encouraging the use of recycled materials and promoting efficient resource management, this criterion helps to minimize the environmental impact of construction activities. It also supports a circular economy by promoting the reuse and recycling of materials.
Indoor Environmental Quality:
The IGBC rating system places a strong emphasis on creating a healthy and comfortable indoor environment. This criterion addresses factors such as air quality, lighting, and thermal comfort. By ensuring high indoor environmental quality, buildings can enhance the well-being and productivity of their occupants, providing a better quality of life and promoting health and comfort within the built environment.
Innovation in Design:
Innovation is encouraged in the IGBC rating system through the innovation in design criterion. This criterion rewards creativity and innovative practices that go beyond standard sustainability criteria. By fostering innovative solutions to sustainability challenges, IGBC encourages projects to push the boundaries of what is possible in green building practices, leading to groundbreaking advancements in the industry.
Regional Priority:
The regional priority criterion considers specific environmental issues or priorities relevant to the local region where the building is located. This ensures that the rating system is adaptable to different environmental contexts and addresses local sustainability challenges effectively. By focusing on regional priorities, the IGBC rating system promotes tailored solutions that are most beneficial for the specific environmental needs of each area.
Achieving certification involves meeting specific criteria within these categories, with points awarded for each criterion. The final rating corresponds to the total points earned, with Certified, Silver, Gold, and Platinum levels indicating increasing levels of sustainability.
Different Rating Systems
- Government Incentives to IGBC Projects
- IGBC Green New Buildings
- IGBC Green Existing Buildings
- IGBC Green Homes
- IGBC Green Residential Societies
- IGBC Green Affordable Housing
- IGBC Green Healthcare
- IGBC Health and Well-being
- IGBC Green Schools
- IGBC Green Resorts
- IGBC Green Factory Buildings
- IGBC Green Data Center
- IGBC Green Interiors
- IGBC Green Service Buildings
- IGBC Green Logistics Parks and Warehouses
- IGBC Green Campus
- IGBC Green Cities
- IGBC Green Existing Cities
- IGBC Green Townships
- IGBC Green SEZs
- IGBC Green Villages
- IGBC Green Landscapes
- IGBC Green Mass Rapid Transit System
- IGBC Green Existing Mass Rapid Transit System
- IGBC Green Railway Stations
- Renewal of IGBC Green Rating
- IGBC Net Zero Energy Buildings
- IGBC Net Zero Water Buildings
- IGBC Green High-Speed Rail
- IGBC Green Hill Habitat
- IGBC Expedited Review Process
- IGBC Net Zero Waste Rating System
Latest Initiatives of IGBC
IGBC New Rating System
The Indian Green Building Council (IGBC) offers a range of rating systems designed to assess and certify the sustainability of buildings across various categories. These categories include Green Homes (residential), Green Buildings (commercial, industrial, and institutional), Green SEZ (Special Economic Zones), Green Cities (urban development), Green Existing Buildings (retrofitting), and Green Interiors (commercial interiors). Each rating system is tailored to the specific type of project, focusing on holistic sustainability in building and urban development.
Recently, IGBC introduced the new Green New Buildings Rating System, which focuses on aligning with national priorities such as water conservation, waste management, energy efficiency, reducing fossil fuel use, minimizing reliance on virgin materials, and prioritizing occupant health and well-being. This rating system mandates adherence to national standards and codes, aiming to surpass them and set new benchmarks for sustainability.
1. Water Conservation: The new rating system aims to save 30-50% of potable water through strategies that promote self-sustainable usage. This includes rainwater harvesting, greywater recycling, and the use of water-efficient fixtures to reduce overall water consumption.
2. Handling of Consumer Waste: By encouraging waste segregation at the source, the system addresses the significant challenge of municipal waste management. Proper segregation and disposal of waste help in reducing landfill pressure and promoting recycling and composting practices.
3. Energy Efficiency: Emphasizing the use of energy-efficient building components, the rating system aims for 20-30% energy savings. This includes the integration of energy-efficient lighting, HVAC systems, and the adoption of renewable energy sources like solar power.
4. Reduced Use of Fossil Fuels: The system promotes the use of alternative fuel vehicles for transportation, thereby reducing the dependence on fossil fuels. Encouraging the use of electric vehicles and providing charging infrastructure are key components of this initiative.
5. Reduced Dependency on Virgin Materials: By encouraging the use of recycled materials, the rating system aims to mitigate the environmental impacts associated with the extraction and processing of virgin materials. This includes using recycled steel, fly ash in concrete, and other sustainable building materials.
6. Health and Well-being of Occupants: The system mandates provisions for proper ventilation, access to natural daylight, and well-being facilities to minimize indoor air pollutants and enhance the overall comfort and health of occupants.
This new rating system is applicable to various types of new buildings, including offices, IT parks, banks, malls, and hospitals. The system classifies buildings based on their ownership—whether they are owner-occupied or tenant-occupied—ensuring that the sustainability measures are relevant and effective for different occupancy scenarios.
IGBC-Nest
The IGBC-Nest initiative is a collaborative effort between the Confederation of Indian Industry (CII) and the Indian Green Building Council (IGBC) aimed at transforming individual homes into sustainable living spaces. This initiative introduces a unique framework and certification tailored specifically for residential units, encouraging homeowners to adopt simple yet impactful green measures.
Key Focus of IGBC's NEST Framework:
1. Green Measures: The framework encourages the adoption of green measures that significantly impact resource efficiency and occupant well-being. These measures include using energy-efficient appliances, installing low-flow water fixtures, and incorporating sustainable landscaping practices.
2. Key Areas: The IGBC Nest framework emphasizes key areas such as the building envelope, water and energy efficiency, and harnessing solar energy. Improvements in these areas lead to substantial reductions in energy and water consumption, enhancing the overall sustainability of the home.
3. GreenPro Ecolabel: This initiative facilitates the selection of appropriate green products for construction by using the GreenPro ecolabel. This label helps homeowners choose materials and products that meet high environmental standards, ensuring that their homes are built or renovated with sustainability in mind.
Certification levels under the IGBC Nest framework are awarded based on meeting mandatory requirements and earning a minimum of 20 credits. This ensures that homes are not only sustainable but also meet high standards of environmental performance.
IGBC's Efforts in Green Building Awareness; Collaborative Approach to Sustainability
The Indian Green Building Council (IGBC) has made significant strides in transforming the green building sector. The impact of the body extends beyond the numerical count, representing a fundamental shift in the industry towards environmentally conscious and responsible building standards. IGBC's efforts in consolidating these achievements set the stage for further advancements in the realm of sustainable real estate.
Government Support and Policy:
The symbiotic relationship between IGBC and government initiatives, such as the Smart Cities Mission and Green Infrastructure Initiative, is pivotal in fostering green building practices. The alignment of objectives creates an environment conducive to sustainable construction. Analyzing the evolving policy landscape provides insights into future developments, ensuring that regulatory frameworks continue to support and incentivize eco-friendly building practices, solidifying IGBC's role as a key player in shaping the industry's trajectory.
Consumer Awareness and Demand:
A fundamental driver of the paradigm shift towards sustainable living is increasing consumer awareness. IGBC recognizes the importance of engaging and educating consumers in sustainable practices. Actively involving the public in the green building movement, IGBC aims to create a ripple effect where informed consumers advocate for environmentally responsible construction choices. This consumer-driven demand reinforces the industry's imperative to adopt green building practices, emphasizing IGBC's role in shaping consumer preferences.
Global Collaboration and Best Practices:
Recognizing the importance of global collaboration, IGBC actively seeks partnerships to adopt and share best practices in sustainable construction. Fostering relationships and drawing inspiration from successful international examples, IGBC positions itself as a global leader in sustainable development. This collaborative approach ensures a continuous exchange of ideas and the incorporation of proven strategies into the Indian context, contributing to the evolution of green building practices.
Looking Ahead to 2024
IGBC's strategic vision for the future includes ambitious goals aimed at significantly increasing the adoption of green building practices in India. One of the primary targets is to certify 10,000 green buildings by 2024. This target reflects a proactive approach in promoting sustainability within the industry, leveraging heightened awareness and collaborative efforts with stakeholders.
Key Initiatives for 2024:
1. Increasing Project Registrations and Coverage: IGBC aims to expand its reach by increasing project registrations across diverse regions. This involves engaging with various stakeholders, including developers, government bodies, and local communities, to promote the benefits of green building certification.
2. Enhancing Green Building Ratings Variety: To cater to evolving project typologies, IGBC plans to introduce and refine its rating systems. This includes developing new criteria and guidelines that address the unique challenges and opportunities of different types of buildings and urban developments.
3. Growing Membership and Collaboration: IGBC is committed to expanding its membership base and fostering collaboration with a broad spectrum of stakeholders. This includes architects, engineers, developers, policymakers, and environmental organizations. By building a strong network of green building advocates, IGBC can drive more significant change in the industry.
4. Training and Qualifying Professionals: Continuing efforts to train and qualify professionals in green building practices are crucial for strengthening the green building community. IGBC will focus on providing education and certification programs that equip professionals with the knowledge and skills needed to implement sustainable practices effectively.
5. Driving Energy, Water, and Waste Savings: IGBC will continue to emphasize the importance of energy, water, and waste savings in certified projects. This includes promoting best practices and innovative solutions that help buildings reduce their environmental footprint.
6. Promoting Renewable Energy and Reduced CO2 Emissions: The organization will advocate for the installation of renewable energy systems and measures to reduce CO2 emissions. By encouraging the use of solar panels, wind turbines, and other renewable energy technologies, IGBC aims to reduce the reliance on fossil fuels and lower greenhouse gas emissions.
7. Exploring Innovative Approaches: IGBC will explore and promote innovative approaches to sustainability and eco-friendly construction. This includes researching new materials, technologies, and methods that can enhance the environmental performance of buildings and urban developments.
Conclusion
The Indian Green Building Council (IGBC) is at the forefront of promoting sustainable and eco-friendly practices in India's construction sector. Through its certification programs, awareness campaigns, and collaborative initiatives, IGBC is transforming the industry's landscape. As IGBC envisions a future where sustainable construction is the norm, its proactive approach positions it as a key influencer in shaping a more responsible and sustainable built environment in India.
Images- thecsrjournal.in,/igbc.in, zenatix.com









.png)