In the realm of real estate, technological advancements have revolutionized the way properties are marketed, transactions are conducted, and decisions are made. One such innovation that has gained prominence is real estate mapping technology, powered by Geographic Information Systems (GIS). This technology not only provides a visual representation of properties but also offers invaluable insights that can elevate the real estate business to new heights.
Understanding Real Estate Mapping Technology:
Real estate mapping technology involves the utilization of GIS to generate comprehensive maps that integrate various data layers. These maps offer detailed insights into specific locations, aiding stakeholders in making informed decisions regarding property investments, developments, and marketing strategies.

Applications of Real Estate Mapping Technology:
1. Spatial Analysis: Real estate professionals utilize spatial analysis to assess market dynamics, evaluate potential investment opportunities, and quantify differences between various locations based on factors such as demographics, market potential, and average prices.
2. Locating Social & Physical Infrastructure: By mapping social and physical infrastructure, including landmarks, transportation networks, and amenities, real estate mapping enables stakeholders to identify advantageous locations for development projects and assess accessibility for customers and employees.
3. Environment & Disaster Impact Assessment: GIS-based mapping facilitates hazard zone mapping, assessing the impact of environmental factors and disasters on properties. This information is crucial for developers to ensure compliance with regulations and mitigate risks.
4. Interactive Property Presentations: Real estate mapping enhances the property search experience for buyers and investors by providing interactive maps with detailed information such as square footage, amenities, and zoning. Virtual tours and 360-degree views further enrich the experience, saving time and resources.
5. Targeted Marketing: With access to demographic data and accurate property information, real estate professionals can create targeted marketing campaigns tailored to specific audiences. High-quality maps can be incorporated into promotional materials to enhance communication and engagement.
Types of Real Estate Mapping Technology
1. Geographic Information Systems (GIS):
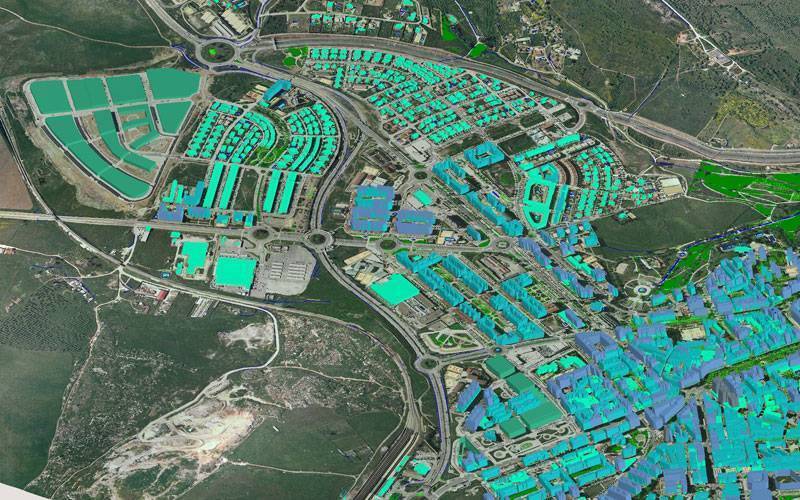
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) are powerful tools that integrate various data layers onto a map, enabling users to analyze and visualize spatial relationships. Real estate professionals use GIS for a wide range of applications, including property assessment, zoning analysis, market research, and demographic studies. By overlaying data such as property boundaries, land use, demographics, and infrastructure, GIS helps in making informed decisions about property development, investment, and management. It provides insights into market trends, helps identify potential risks, and supports efficient resource allocation.
2. Remote Sensing:
Remote sensing technology involves capturing information about the Earth's surface without making physical contact. This is typically done through techniques like aerial photography, satellite imagery, and LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging). In real estate, remote sensing data provides valuable insights into land use, topography, vegetation, and environmental factors. It aids in site selection, land management, and environmental impact assessment for development projects. By analyzing remotely sensed data, real estate professionals can identify potential development sites, assess property conditions, and monitor changes over time.
3. Geographic Positioning Systems (GPS):
Geographic Positioning Systems (GPS) technology enables precise location tracking, which is essential for real estate applications such as property surveys, navigation, and asset management. GPS devices and mobile apps allow users to accurately determine their position on the Earth's surface, making it easier to locate properties, navigate to them, and conduct field surveys. Real estate professionals use GPS data to map property boundaries, track assets, and provide location-based services to clients. GPS technology also plays a crucial role in property management, facilitating tasks like fleet tracking, route optimization, and geotagging property information.
4. Mobile Mapping:
Mobile mapping solutions utilize mobile devices equipped with GPS, cameras, and sensors to collect geospatial data in the field. Real estate professionals use mobile mapping apps to conduct property inspections, gather site data, and update property information on the go. These tools streamline data collection processes, improve accuracy, and increase efficiency in field surveys and asset management tasks. By leveraging mobile mapping technology, real estate agents, surveyors, and property managers can access location-based information, capture property details, and collaborate with colleagues in real-time, ultimately enhancing productivity and decision-making.
Benefits of Real Estate Mapping Technology in India:
1. Enhanced Urban Planning: Real estate mapping technology provides urban planners with detailed spatial data, allowing for more informed decisions regarding land use, infrastructure development, and zoning regulations. By analyzing factors such as population density, transportation networks, and environmental considerations, planners can optimize city layouts, improve resource allocation, and enhance overall livability.
2. Improved Property Registration: Digital property registries, enabled by real estate mapping, streamline the registration process for land and property transactions. By digitizing cadastral maps and property records, authorities can ensure transparency, reduce administrative burdens, and minimize instances of fraud or disputes. This not only benefits property owners but also promotes investment confidence and legal certainty in the real estate market.
3. Optimized Infrastructure Development: GIS-based mapping tools aid in identifying suitable sites for infrastructure projects such as roads, utilities, and public facilities. By analyzing spatial data on population distribution, traffic patterns, and economic activity, policymakers can prioritize investments in areas with the greatest need and potential for growth. This leads to more efficient infrastructure development, improved service delivery, and enhanced quality of life for residents.
4. Environmental Management: Real estate mapping technology facilitates environmental impact assessments and natural resource management. By mapping ecologically sensitive areas, water bodies, and wildlife habitats, authorities can make informed decisions to minimize environmental degradation and conserve biodiversity. Additionally, GIS enables the monitoring of pollution levels, land degradation, and deforestation, supporting sustainable development practices and regulatory compliance.
5. Disaster Preparedness and Response: GIS mapping plays a crucial role in disaster preparedness, mitigation, and response efforts. By mapping hazard-prone areas, vulnerable populations, and critical infrastructure, authorities can develop evacuation plans, allocate resources effectively, and coordinate emergency response operations. Real-time data visualization and spatial analysis tools enable rapid decision-making during crises, ultimately saving lives and minimizing property damage.
6. Efficient Land Use Management: Real estate mapping facilitates efficient land use planning and management by identifying underutilized or vacant land parcels for redevelopment or revitalization. By analyzing land ownership, zoning regulations, and market trends, policymakers can incentivize responsible land use practices, promote mixed-use development, and address urban sprawl. This optimizes land utilization, enhances property values, and fosters sustainable urban growth.
7. Inclusive Development: Real estate mapping technology empowers local communities and stakeholders to participate in the planning and decision-making process. Through participatory mapping initiatives, residents can contribute local knowledge, identify priority areas for investment, and advocate for their needs. This fosters social inclusion, empowers marginalized communities, and ensures that development initiatives align with the aspirations and interests of all citizens.
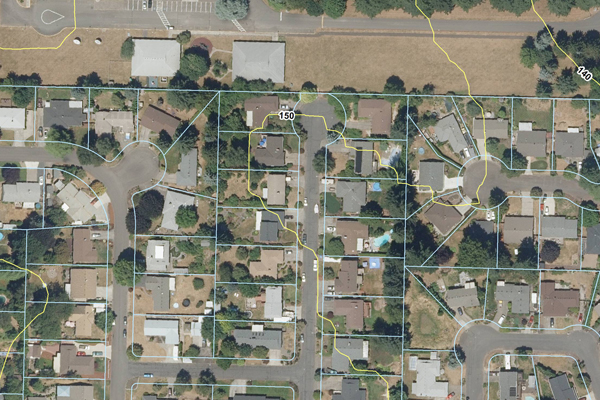

Examples showcasing the advantages of Real Estate Mapping Technology across India:
1. Property Tax Assessment in Bengaluru, Karnataka:
In Bengaluru, the Bruhat Bengaluru Mahanagara Palike (BBMP) faced challenges with property tax assessment due to inaccuracies in property records and difficulties in identifying taxable properties. To address these issues, the BBMP implemented a GIS-based property tax management system. Through real estate mapping technology, the BBMP created digital cadastral maps and property registries, enabling accurate assessment of property taxes based on factors such as property size, location, and usage. The implementation of real estate mapping resulted in increased tax compliance, improved revenue collection, and enhanced transparency in property taxation processes.
2. Smart City Planning in Visakhapatnam, Andhra Pradesh:
Visakhapatnam, a designated Smart City in Andhra Pradesh, utilized real estate mapping technology to support urban planning and development initiatives. By integrating GIS mapping tools with demographic data, infrastructure networks, and environmental parameters, the Visakhapatnam Municipal Corporation identified priority areas for investment, infrastructure improvement, and public service delivery. Real estate mapping facilitated the development of Smart City projects such as intelligent transportation systems, digital governance platforms, and sustainable urban infrastructure, contributing to the city's economic growth and quality of life.
3. Land Acquisition for Infrastructure Projects in Mumbai, Maharashtra:
The Mumbai Metropolitan Region Development Authority (MMRDA) leveraged real estate mapping technology to streamline the process of land acquisition for infrastructure projects such as metro rail expansion and road widening. Using GIS mapping tools, the MMRDA conducted land surveys, identified land parcels for acquisition, and assessed property values based on market trends and spatial data analysis. Real estate mapping facilitated transparent and efficient negotiations with landowners, minimized delays in project implementation, and optimized land utilization for critical infrastructure development in Mumbai's metropolitan region.
4. Rural Development Planning in Kerala:
The Government of Kerala utilized real estate mapping technology to support rural development planning and land management initiatives in the state's rural areas. By digitizing cadastral maps and land records, Kerala's Revenue Department improved land tenure security, facilitated land transactions, and prevented encroachments on public lands.
These examples demonstrate the diverse applications and benefits of real estate mapping technology across different regions and sectors in India. From urban governance and infrastructure development to disaster management and rural planning, GIS-enabled solutions have the potential to drive positive change and foster sustainable development outcomes nationwide.
Future Outlook:
GIS-enabled real estate mapping holds immense potential for the Indian real estate industry. As adoption grows, stakeholders can leverage this technology to enhance customer experiences, formulate strategic investment plans, and promote sustainable development practices. By embracing GIS-based mapping solutions, real estate professionals can unlock new opportunities and navigate the complexities of the ever-evolving real estate landscape with confidence.
Conclusion
Real estate mapping technology has emerged as a transformative tool with diverse applications and significant advantages across various regions and sectors in India. From enhancing transparency and efficiency in property registration and taxation processes to supporting urban planning, infrastructure development, and disaster management initiatives, GIS-enabled solutions have revolutionized the way stakeholders approach real estate and land management. The examples highlighted in this article demonstrate the tangible benefits of real estate mapping, including increased revenue generation, improved service delivery, and enhanced resilience to natural disasters. As India continues to embrace technological innovations and digital solutions in the real estate sector, the integration of real estate mapping will play a pivotal role in driving sustainable development, promoting inclusive growth, and creating thriving, resilient communities across the country.
Images- bloomberg.com, clackamas, harrisonburghousingtoday.com,polosoftech.com









.png)