In modern construction, achieving successful project outcomes requires balancing efficiency, budget control, and safety—all of which depend on quick access to key data. Traditionally, construction data like as-built drawings, safety guidelines, and project visuals are stored separately, creating challenges in retrieval and coherence. Geographic Information Systems (GIS) address this by integrating and organizing project data onto interactive, geospatial maps. By using GIS, construction teams can access project data quickly and visually, leading to more informed decision-making and smoother project management.
What is GIS, and How it is Utilized in Construction?
GIS is an advanced mapping technology that captures, stores, and analyzes spatial data to display information on site maps, which provides construction teams with a practical way to view project data and details at a glance. With GIS, multiple data types can be organized into “layers,” giving users access to a cohesive overview that aids project planning, risk assessment, and real-time updates. These layers provide visual cues to the location and status of various project elements, such as infrastructure layouts, topography, and environmental conditions, allowing for better coordination and more precise adjustments as the project progresses.

Key Data Types in GIS for Construction
As-Builts, Redlines, and Site Plans: GIS stores final project layouts and updates, known as as-builts and redlines, for quick reference. This information is critical in managing assets, performing post-project audits, and supporting future modifications.
Topographic and Environmental Information: Satellite images, UAV data, or surveys can supply topographic information, showing details like elevation changes and soil composition, while environmental data highlights constraints like flood zones and protected habitats. This data is essential in ensuring compliance with environmental regulations and anticipating possible natural obstacles.
Project Management Data: Linking project tasks to specific locations within GIS allows teams to visualize progress, allocate resources effectively, and track completion statuses. This layer serves as a comprehensive tool for coordinating equipment, materials, and workforce.
Infrastructure Layers: GIS offers detailed maps of existing infrastructure like roads, pipelines, and power lines. Integrating this data reduces planning errors, minimizing disruptions to essential services and enabling more efficient site layouts.
Punch Lists and Inspections: GIS organizes punch lists and inspections by specific site areas, showing where outstanding tasks or corrective actions are required. This visibility supports a smoother project closeout and enhances quality control.
Safety Data: GIS records and visualizes safety-related data, such as locations with high accident rates, enabling teams to identify potential risks and proactively improve safety measures.
Visual Documentation: Photos and videos linked to specific site areas through GIS assist in tracking site conditions and milestones, offering quick, visual insights that make inspection and progress evaluation more efficient.
Material Data: GIS can track material specifications, maintenance needs, and warranties, helping with future facility management and allowing quick access to information for replacement or repairs.
The Benefits of GIS in Construction
Efficient Progress Tracking: GIS visually represents project progress, enabling real-time updates on completed tasks and issue areas. This visual tracking reduces delays by allowing project leaders to promptly address any deviations from the plan.
Proactive Risk Management: Analyzing safety data in GIS allows construction teams to identify trends and take preventive actions. For example, if specific locations see recurrent incidents, teams can apply additional safety measures or adjust workflows to avoid risks.
Enhanced Site Selection and Analysis: GIS facilitates site selection by merging environmental, regulatory, and logistical data. This capability assists developers in choosing optimal sites while anticipating challenges related to zoning, environmental impact, or resource availability.
Precision in Design and Planning: GIS provides real-time site information, which design teams can use to fine-tune project plans. By visualizing the current conditions and resources at the site, GIS ensures that construction proceeds smoothly and accurately.
Optimized Site Management: GIS improves onsite management by providing clear directions and material placement maps. A centralized, accurate map minimizes miscommunication, ensuring workers and resources are correctly allocated.
Streamlined Collaboration: GIS enables easy tagging and sharing of documents like RFIs, inspection results, or design updates, minimizing the time lost in retrieving and sharing information among teams.
Environmental Impact Mitigation: GIS helps identify sensitive environmental zones, guiding construction plans to comply with ecological standards. By visualizing features like floodplains, habitats, and preservation sites, developers can avoid costly environmental compliance issues.
Infrastructure Transparency: Viewing existing infrastructure in GIS aids in preventing accidental damage to utilities, enhancing regulatory compliance and ensuring efficient workflow.
Long-Term Asset Management: GIS consolidates essential information—like warranty records and maintenance logs—into a central, map-based database. This record-keeping supports informed decisions on repairs, upgrades, and maintenance, which is valuable for both property owners and managers.
Integrating GIS with Other Technologies
GIS gains greater utility when integrated with complementary technologies, creating a unified data environment that enhances every stage of construction:
Construction Management Software: Combining GIS with construction management platforms enables teams to manage spatially organized documents, improving workflow by reducing redundancy and increasing data accuracy.
Building Information Modeling (BIM): GIS and BIM together offer a comprehensive view of projects, combining geographic data with structural and architectural details. This integration enables adjustments to design and operations based on real-time geographic data.
Computer-Aided Design (CAD): Merging CAD with GIS improves accuracy in planning by overlaying CAD layouts onto GIS site maps, helping to avoid spatial misalignments during construction.
Drone and UAV Data: GIS benefits from high-resolution imagery and 3D models captured by UAVs, allowing teams to monitor site conditions, track progress remotely, and conduct efficient inspections.
GIS Market Growth and Trends (2024-2028): Global and Indian Outlook
As per Technavio report, the global GIS market is poised for impressive growth, projected to increase by USD 21.57 billion with a CAGR of 20.89% from 2023 to 2028. This growth is fueled by transformative trends such as the integration of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) with Building Information Modeling (BIM), enhancing spatial analysis and visualization capabilities. This convergence is particularly impactful in fields like urban planning, infrastructure development, and construction, where informed decision-making depends on precise geospatial insights. GIS technology is also becoming essential in disaster management, providing critical spatial data that supports emergency response, risk assessment, and recovery initiatives.
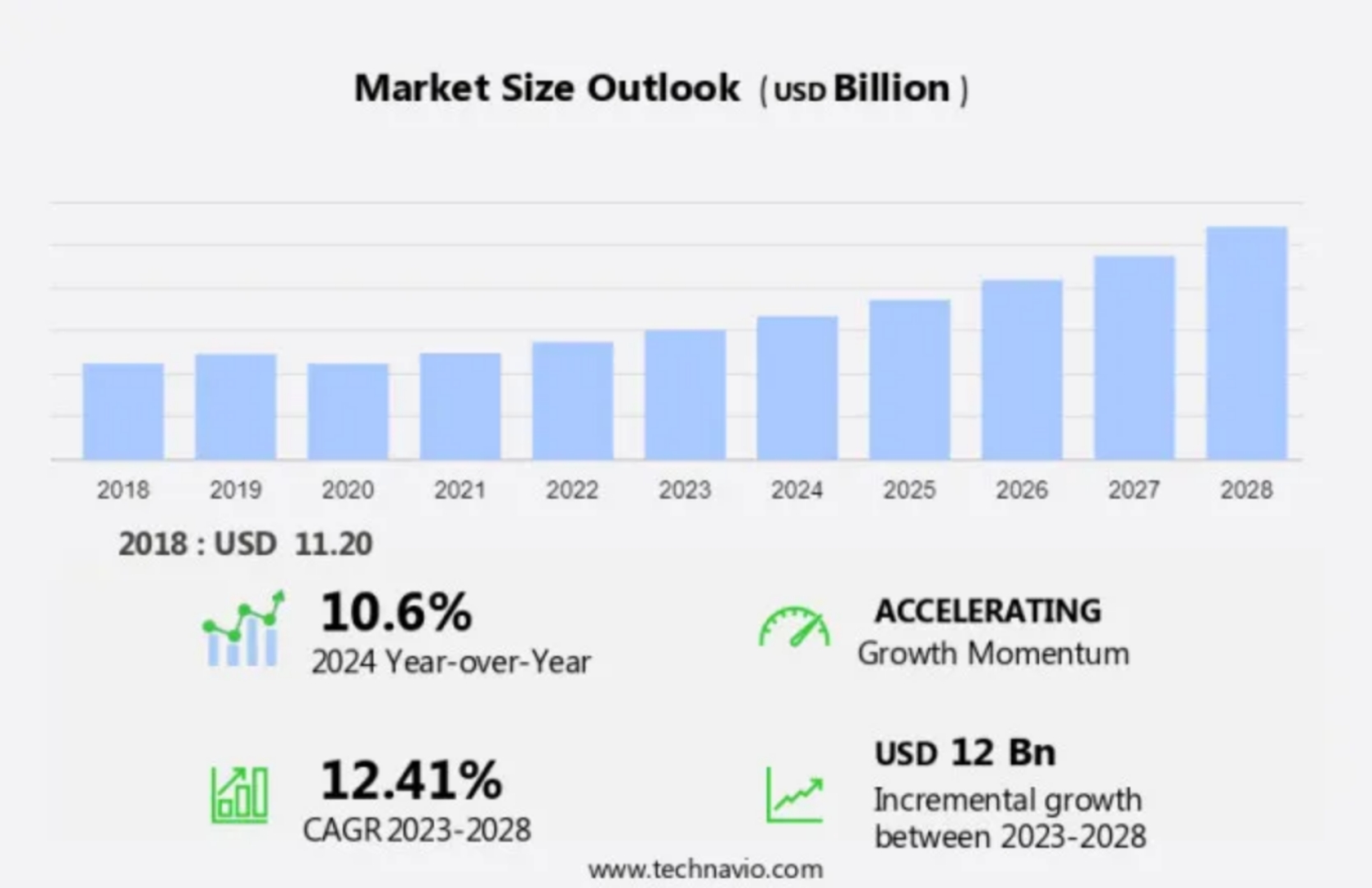
In India, the GIS market is also expanding rapidly, driven by government initiatives like Digital India, Smart Cities Mission, and National Geospatial Policy. These initiatives emphasize the value of geospatial intelligence for sustainable development, urban planning, and rural digitization. The adoption of GIS in disaster management is particularly significant in India, where frequent natural disasters make real-time spatial data essential for effective emergency response and risk mitigation.
Conclusion
GIS is transforming construction project management by centralizing spatial data on interactive maps, allowing for better decisions at every project stage. By making project information accessible and organized, GIS optimizes operations, enhances safety, and improves team collaboration. As GIS technology evolves, its impact on the construction industry will grow, enabling teams to address challenges with precision and preparing the industry for a future that demands data-driven, sustainable construction practices.









.png)