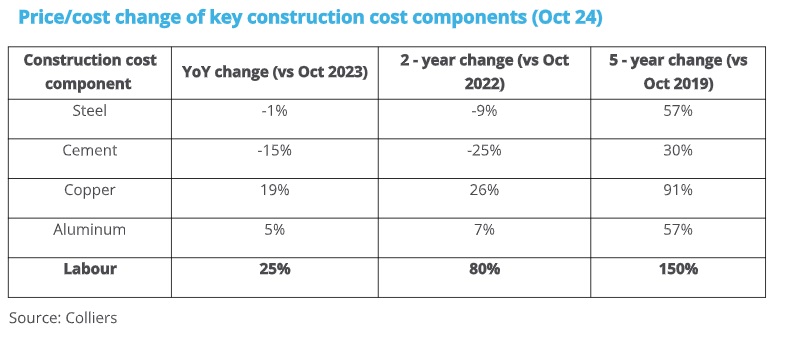
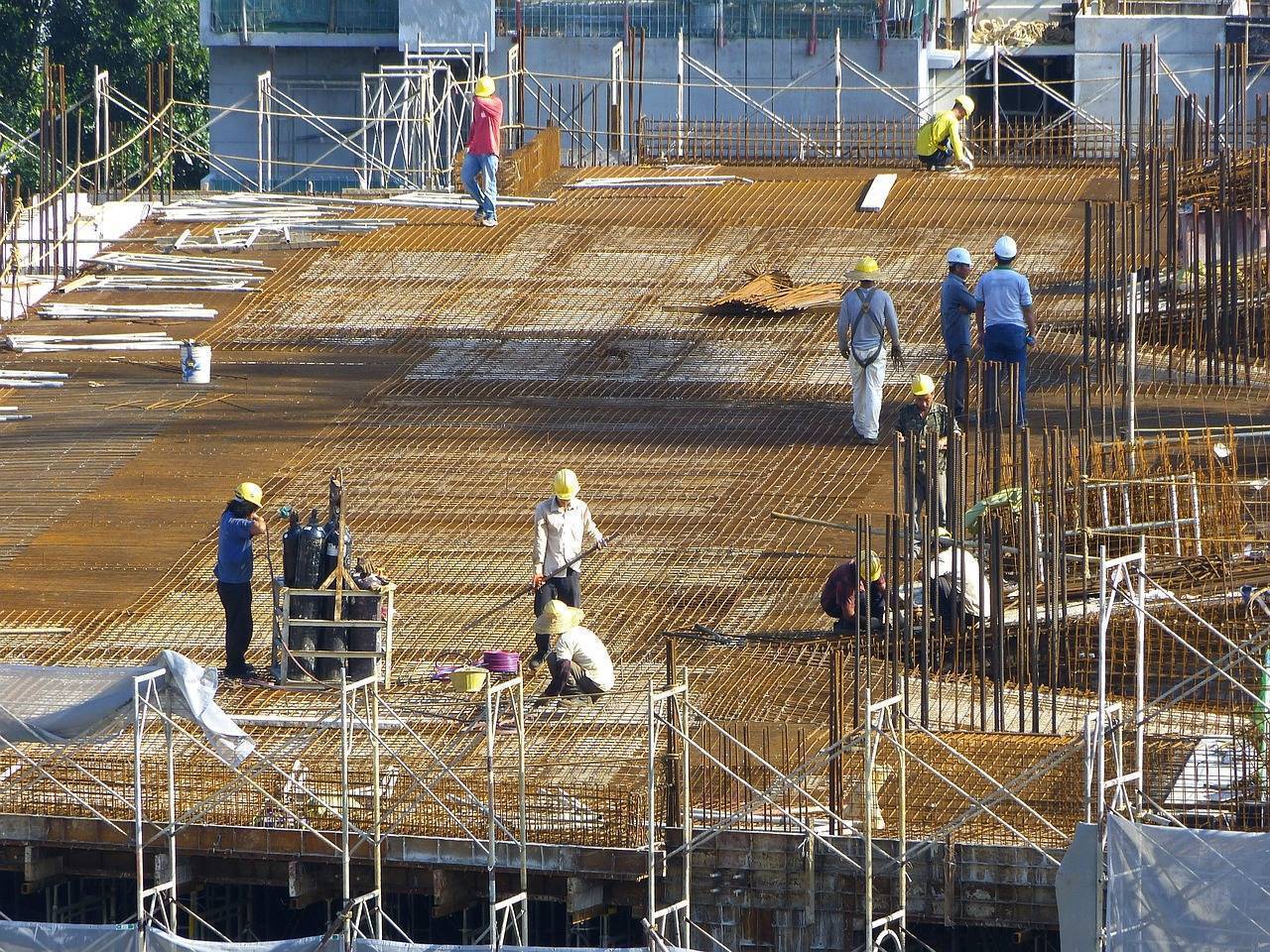
Over the past year, the average cost of construction has risen by up to 11%, primarily driven by a significant surge in labour costs and moderate price increases in construction materials such as sand, brick, glass, and wood. According to Colliers, the pace of price hikes for key construction materials, including cement, steel, copper, and aluminum, has slowed in 2024 across major real estate markets. Notably, cement prices have declined by 15%, while steel prices have seen a marginal decrease of 1% over the last 12 months.
Despite these declines, overall construction costs have continued to rise due to the sharp increase in labour costs, along with moderate hikes in fuel prices and materials like aluminum, copper, sand, and wood. The residential sector, in particular, has been most affected by these cost increases.
Impact of rising labour cost
Rising labour costs are also having a substantial impact on construction expenses. The increasing demand for construction workers, particularly in major cities, is driving up labour rates. With the high demand for homes, offices, shopping malls, retail outlets, and industrial warehouses, labour retention and accommodation costs have become critical during the construction phase. Additionally, the rising cost of living in urban areas, coupled with regulatory changes focused on improving worker welfare, is contributing to escalating labour costs. As a result, these factors are stretching construction budgets, increasing operational expenses, and leading to higher overall project costs.
“While the rise in prices of key construction materials was relatively modest over the last year, labour costs have been driving the overall cost of construction upward. With labour accounting for more than one-fourth of overall construction cost, a 25% annual rise in labour costs has stretched construction budgets and impacted operational expenses. Moreover, the need for skilled labour and the associated costs for training, safety and regulatory compliance further adds to spiraling labour costs.” said Badal Yagnik, Chief Executive Officer, Colliers India.
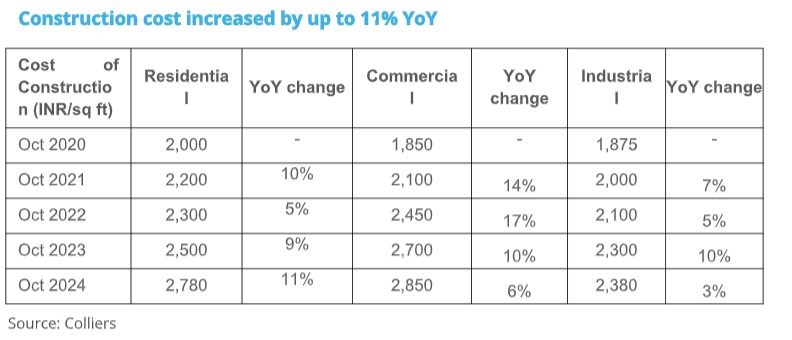
Cost of construction surges highest in the residential segment
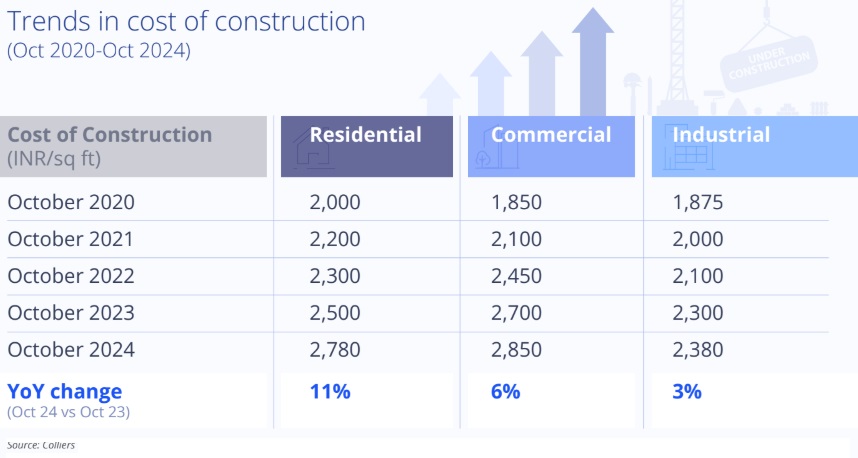
As of October 2024, cost of construction in the residential segment saw an estimated 11% increase YoY. Amongst various real estate segments, construction cost escalation has been relatively sharper in the residential segment. Interestingly, increasing built quality consciousness and the growing demand for amenity rich gated communities have persuaded residential developers to upscale their real estate offerings in general and thus led to higher cost of construction in the residential segment.
“Despite rising construction costs across real estate segments, the commercial and industrial & warehousing segments have witnessed robust new supply during 2024. For instance, the Indian office market saw 37 million square feet of new completions in the first nine months of 2024, while the industrial & warehousing segment saw about 22 million square feet of new supply. Amidst healthy demand especially for Grade A developments, project completions are expected to be largely on schedule across major cities. Real estate developers, meanwhile, are likely to step-up technology and sustainability adoption across asset classes.” says Vimal Nadar, Senior Director and Head of Research, Colliers India.
To manage the steady rise in overall construction costs and related challenges, developers are optimizing expenses by reassessing budgets. They are focusing on improving supply chain management by diversifying suppliers and opting for localized sourcing of key construction materials. Additionally, real estate developers are investing in training and automation to tackle issues related to the availability of skilled manpower, which can improve project scheduling. Moving forward, greater adoption of the circular economy will help optimize construction costs, enhance efficiency, and support sustainability.









.png)