As sustainability becomes a key focus in construction and real estate, Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design (LEED) has emerged as the most widely used green building certification system worldwide. Developed by the U.S. Green Building Council (USGBC), LEED provides a framework for healthy, highly efficient, and cost-saving green buildings. Whether for commercial spaces, residential homes, or entire communities, LEED certification serves as a globally recognized symbol of sustainability achievement.
With environmental concerns such as climate change, energy consumption, and resource depletion becoming increasingly pressing, green building certifications like LEED are reshaping urban landscapes. The impact of LEED is multifaceted, influencing not just the buildings but also their occupants, surrounding communities, and overall market trends.
What is LEED Certification?
LEED is the most widely used green building rating system in the world, offering a framework for healthy, efficient, and cost-saving green buildings. It applies to virtually all building types, including new construction, interiors, operations, maintenance, and core and shell projects. LEED certification is a globally recognized symbol of sustainability achievement and leadership.
LEED-certified buildings incorporate sustainable features such as energy-efficient HVAC systems, water-saving technologies, and environmentally friendly materials. These elements significantly reduce resource consumption and greenhouse gas emissions while enhancing operational efficiency. The certification provides a structured process to achieve sustainability goals and has been a catalyst for innovation in the real estate and construction sectors.
India’s Leadership in LEED Zero Certification
India has emerged as a global leader in LEED Zero certifications, surpassing both the U.S. and China. LEED Zero recognizes projects that have achieved net zero or net positive status in carbon, energy, water, or waste.
With 73 LEED Zero-certified projects, India accounts for 45% of the more than 150 global LEED Zero certifications. Haryana and Tamil Nadu are leading in these certifications. Comparatively, the U.S. holds 47 LEED Zero certifications (30%), while China follows with 15 certifications (10%).
Notably, DLF is the global leader in total LEED Zero certifications, with 45 certified projects, followed by ITC Group with 15 certifications. The private sector’s active participation highlights India’s commitment to sustainable building solutions.
LEED Rating Levels
LEED certification is awarded at different levels based on the number of points a project earns. These levels include:
- Certified (40–49 points)
- Silver (50–59 points)
- Gold (60–79 points)
- Platinum (80+ points)
LEED Rating Systems
LEED offers multiple rating systems tailored to different project types:
- LEED for Building Design and Construction (BD+C): For new construction and major renovations.
- LEED for Interior Design and Construction (ID+C): For tenant improvements and interior fit-outs.
- LEED for Building Operations and Maintenance (O+M): For existing buildings undergoing sustainable upgrades.
- LEED for Neighborhood Development (ND): For entire communities focusing on sustainability.
- LEED for Homes: For residential properties, promoting energy efficiency and sustainability in single-family and multi-family homes.
The Evolution of LEED and Its Global Adoption
Since its launch in 1998, LEED has evolved to address new building types, advancements in sustainable technology, and global environmental challenges. Initially focused on energy efficiency, LEED has now expanded to include carbon neutrality, biodiversity, and occupant well-being.
LEED is widely adopted across the globe, with thousands of projects in the U.S., Canada, India, China, and Europe. Countries like India have become global leaders in LEED Zero projects, surpassing the U.S. and China in net-zero certified green buildings. Major companies like DLF and ITC are at the forefront of this transformation.
Notable LEED-Certified Projects in India
Several Indian projects exemplify the success of LEED certification:
1. DLF Cyber City, Gurugram

(Source: dlf.in)
Certification: LEED Zero Water (First portfolio globally certified)
Key Features:
- 13.8-million-square-foot commercial campus with 16 buildings
- Rainwater harvesting system with over 100 recharge pits
- On-site sewage treatment plants for water recycling
- Tenant engagement programs promoting water conservation
Impact: A benchmark for sustainable office spaces in India, encouraging Fortune 500 companies to operate in green-certified buildings.
2. ITC Windsor, Bengaluru
(Source: itchotels.com)
Certification: LEED Zero Carbon (First hospitality project globally to achieve this)
Key Features:
- Energy-efficient design integrating renewable energy sources like solar and wind
- Sustainable operations reducing carbon footprint beyond regulatory requirements
- Environmentally responsible travel initiatives for eco-conscious guests
Impact: Sets a new standard in sustainable luxury hospitality, proving that high-end hotels can achieve net zero carbon goals.
3. One Trade Tower, Bengaluru (Nucleus Office Parks)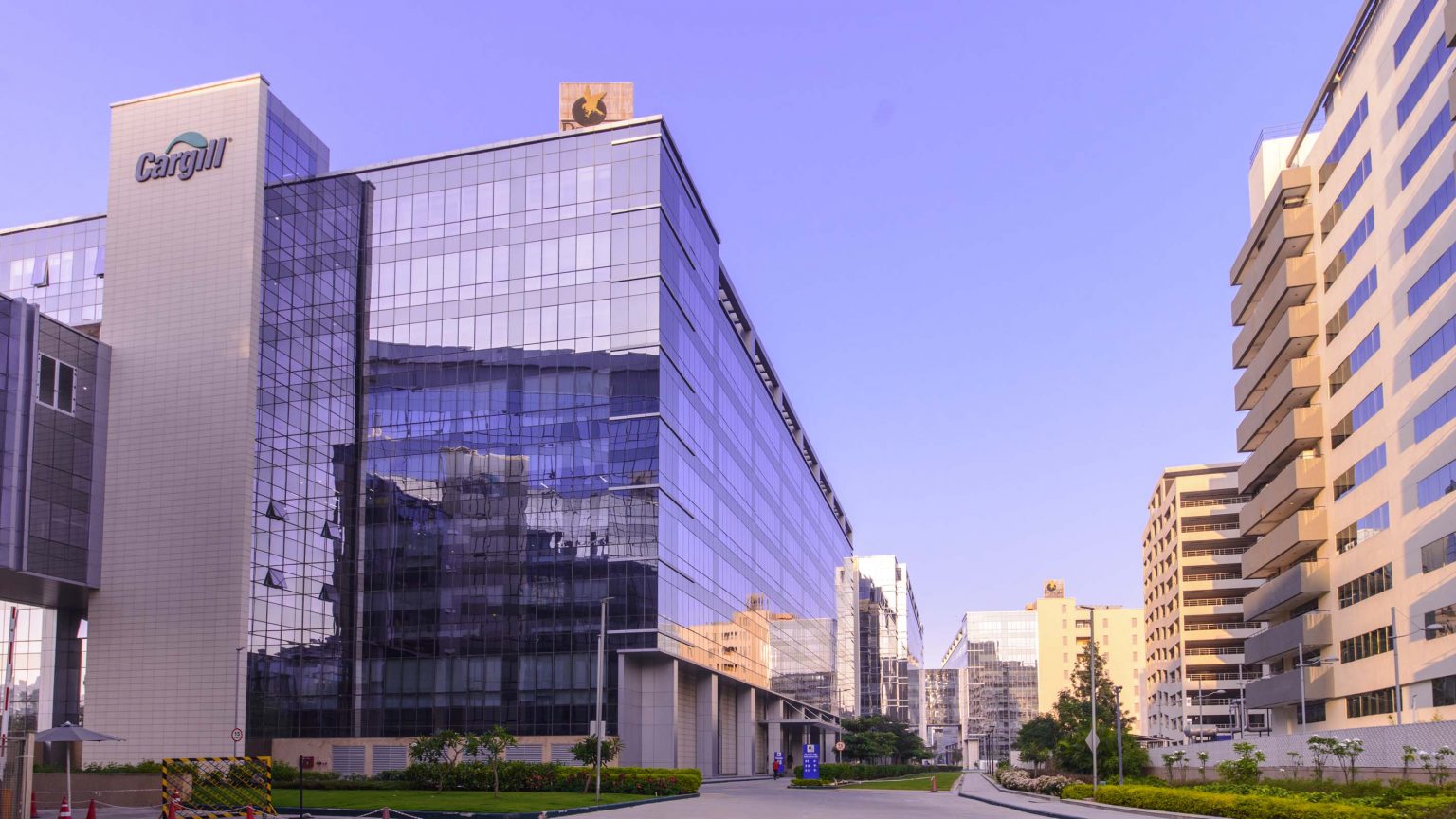
(Source: commercialdesignsindia.com)
Certification: LEED Zero Carbon & LEED Zero Energy
Key Features:
- Advanced energy monitoring systems for optimizing consumption
- Investments in renewable energy sources to offset carbon emissions
- Indoor air and water quality improvements for occupant health
- EV charging stations and organic waste composting facilities
Impact: Showcases how commercial office buildings can lead the way in achieving net zero performance, influencing other properties to follow suit.
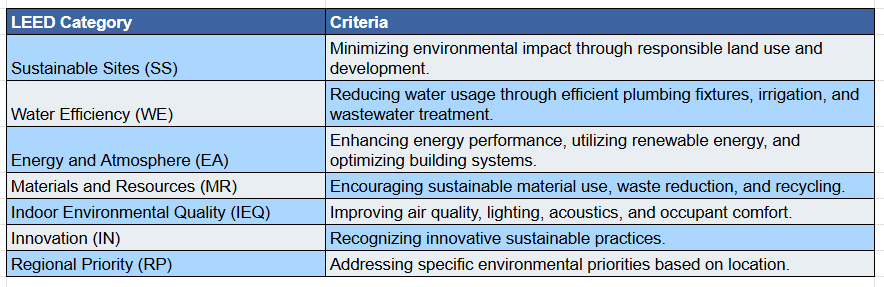
Key LEED Categories and Criteria
The Transformative Power of LEED Certification
The impact of LEED certification extends beyond reducing carbon footprints—it enhances urban aesthetics, boosts economic advantages, and improves community well-being.
1. Environmental Benefits
- LEED-certified buildings incorporate sustainable materials and energy-efficient technologies, significantly reducing carbon emissions.
- Water-saving innovations help address water scarcity concerns, a critical issue in rapidly urbanizing regions like India.
- Renewable energy integration, including solar and wind power, reduces dependence on fossil fuels.
2. Architectural and Urban Aesthetic Impact
- LEED-certified buildings contribute to futuristic urban skylines, blending eco-friendly design with aesthetic appeal.
- Green-certified projects encourage urban renewal, inspiring older buildings to retrofit their structures to meet sustainability standards.
3. Economic and Business Advantages
- LEED-certified buildings reduce operational costs by lowering energy and water consumption.
- Sustainable projects often experience higher property values, attracting investors and businesses.
- India’s commitment to LEED Zero aligns with the country’s goal of achieving net zero greenhouse gas emissions by 2070.
The LEED Certification Process
1. Registration: Project teams must register their building with the USGBC and pay a registration fee.
2. Documentation & Compliance: Teams submit documentation proving compliance with LEED criteria. This includes energy modeling, water efficiency plans, and waste management strategies.
3. Review & Certification: The USGBC reviews the submissions and assigns a certification level based on the achieved points.
Challenges in Achieving LEED Certification
- High Initial Costs: Sustainable materials and technologies require upfront investment.
- Complexity: The certification process can be technical and time-consuming.
- Stringent Requirements: Meeting LEED standards requires expertise in green building practices.
However, the long-term benefits in energy efficiency, cost savings, and marketability make LEED a valuable investment.
Government and Corporate Role in Promoting LEED
India’s government, in collaboration with industry leaders, is taking proactive steps to promote green building certifications:
- Policy Support: Incentives and regulatory support for green construction projects.
- Public-Private Partnerships: Collaboration between government agencies and private developers to implement sustainable building practices.
- Corporate Responsibility: Companies like DLF, ITC, and Wipro are setting benchmarks for sustainability in real estate and commercial spaces.
Future of LEED and Green Building Innovations
As environmental concerns intensify, LEED continues to evolve to address global challenges. Future advancements include:
- Net-zero energy buildings to minimize carbon emissions.
- Integration with smart technologies for enhanced efficiency.
- Expansion in developing nations to promote sustainable urbanization.
With governments, corporations, and individuals recognizing the value of green development, LEED-certified buildings will shape a more sustainable, healthier future.
LEED certification has become a benchmark for sustainable construction, offering environmental, economic, and social benefits. While the process can be complex and costly, the long-term advantages in energy efficiency, cost savings, and improved occupant well-being make it a worthwhile investment.
India’s leadership in LEED Zero certification underscores its commitment to sustainability, with major players like DLF and ITC driving the change. As green buildings gain momentum, LEED-certified projects will play a crucial role in reducing carbon footprints, enhancing urban resilience, and fostering economic growth.
For developers, architects, and investors, integrating LEED principles enhances marketability, operational efficiency, and environmental stewardship—ensuring long-term success in an increasingly eco-conscious world.









