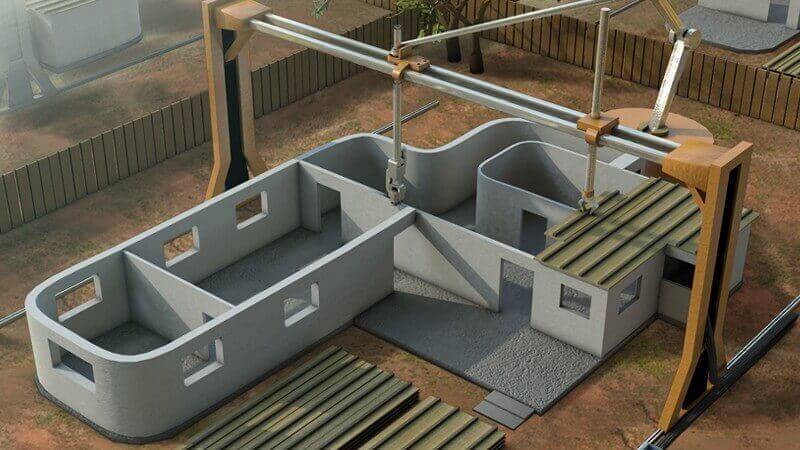
3D printing in construction is a groundbreaking technology that revolutionizes traditional building methods. This innovative approach involves the layer-by-layer construction of structures using specialized 3D printers, typically utilizing materials like concrete. The process, guided by digital models or blueprints, allows for unprecedented design flexibility, enabling the creation of intricate and unconventional architectural forms. Automation, often through robotic arms or large-scale printers, minimizes the need for extensive manual labor, resulting in faster construction timelines and increased efficiency.
Beyond speed and design flexibility, the cost-effectiveness of 3D printing in construction is noteworthy. While initial investments in the technology can be substantial, the potential for reduced labor and material costs, coupled with quicker construction times, positions 3D printing as a cost-effective and sustainable alternative in the construction industry. This transformative technology holds promise for a wide range of applications, from small-scale structures to more extensive projects, offering a glimpse into the future of efficient and innovative construction practices.
How does 3D printing technology work?
3D printing in construction employs a layer-by-layer additive manufacturing process to build structures. The technology typically follows these key steps:
1. Digital Design: The process begins with the creation of a detailed digital model or blueprint of the intended structure. This digital design serves as the guide for the 3D printing process.
2. Material Preparation: Construction-grade materials, such as concrete or specialized building compounds, are prepared for the 3D printing process. These materials are often formulated to meet structural requirements and facilitate layer-by-layer deposition.
3. Printing Process: Specialized 3D printers, which can range from robotic arms to large-scale construction printers, execute the printing process. The printer precisely deposits the construction material layer by layer according to the digital design. This additive approach allows for the gradual creation of the entire structure.
4. Automation and Precision: Automation plays a crucial role in ensuring precision and efficiency. Robotic arms or other automated systems carry out the construction process, reducing the reliance on manual labor. This precision enhances the accuracy of the final structure.
5. Layer Bonding and Solidification: Each layer of material is deposited in a way that ensures proper bonding with the previous layer. Depending on the construction material, processes like curing or solidification may occur to enhance the structural integrity of the built layers.
6. Completion: Once the 3D printing process is complete, the structure undergoes any necessary finishing touches. This may include additional manual work or the integration of non-printed components, depending on the specific project requirements.
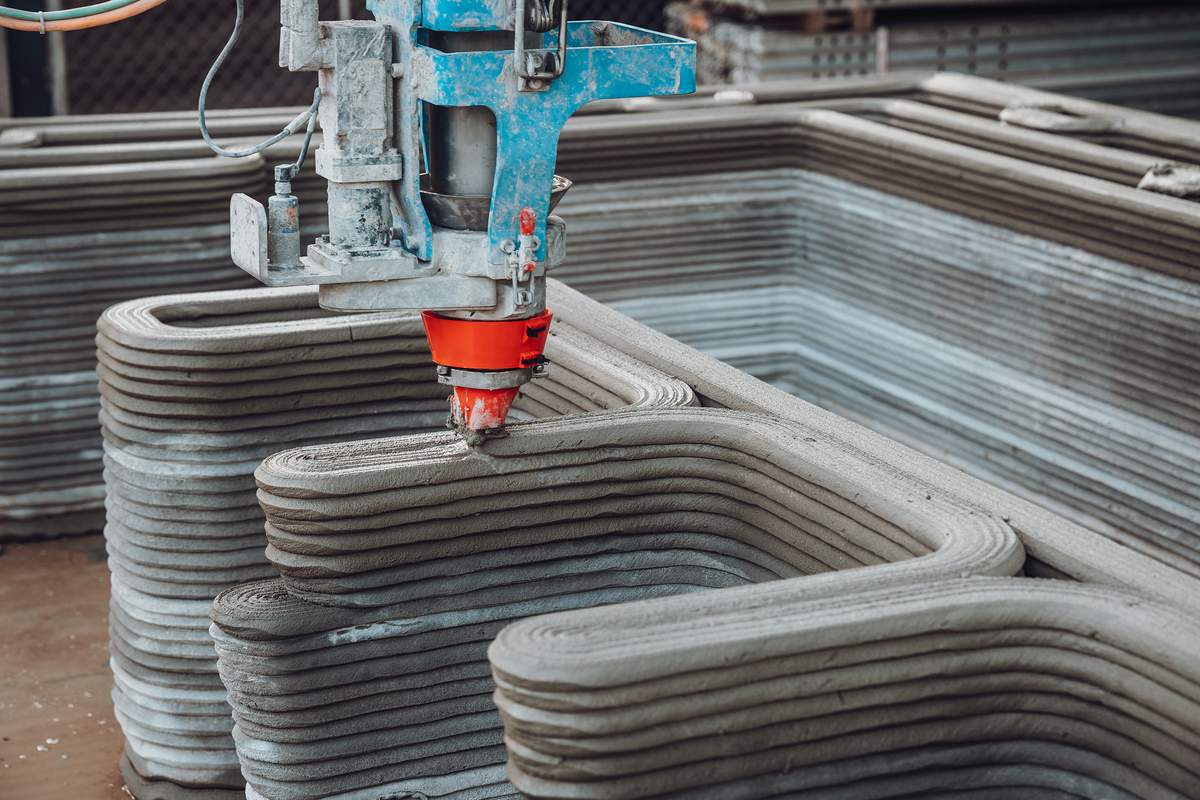

Advantages of 3D printing technology in construction
1. Design Flexibility: 3D printing enables the construction of intricate and unconventional architectural designs that may be challenging or costly with traditional methods. This flexibility allows for the realization of complex and innovative structures.
2. Speed and Efficiency: The layer-by-layer additive construction process significantly accelerates construction timelines compared to traditional methods. Rapid printing and automation contribute to faster project completion, making 3D printing an efficient alternative.
3. Cost-Effectiveness: While the initial investment in 3D printing technology can be substantial, the potential for reduced labor costs, minimal waste, and efficient material usage can lead to overall cost savings in the long run. The technology's efficiency contributes to a more cost-effective construction process.
4. Sustainability: 3D printing in construction often results in less material waste due to precise layering. Additionally, the ability to use sustainable and eco-friendly construction materials enhances the overall environmental sustainability of the building process.
5. Complex Geometries: Traditional construction methods may struggle with complex architectural designs, but 3D printing excels in creating structures with intricate geometries. This capability allows for more creative and customized building solutions.
6. Customization: 3D printing technology enables a high level of customization, catering to specific client requirements. Tailoring designs and structures to meet individual needs is a key advantage, especially in sectors with unique construction demands.
7. Reduced Labor Dependency: The automated nature of 3D printing reduces dependency on manual labor, decreasing the risk of worker-related injuries and addressing potential labor shortages.
8. Consistency and Precision: The automated construction process ensures consistent layering and precision, minimizing errors and discrepancies. This contributes to higher-quality finished structures.
9. Versatility: 3D printing is adaptable to various construction scales, from small-scale structures to larger buildings. Its versatility makes it suitable for diverse applications in the construction industry.
10. Innovation Potential: 3D printing continually opens doors for innovation in construction, with ongoing research and development exploring new materials, techniques, and applications. This technology has the potential to reshape the future of the construction industry.
Applications of 3D printing technology in construction
The versatility of 3D printing in construction has led to its adoption in various applications across the industry. Key applications include:
1. Housing Construction: 3D printing is used to construct entire houses or building components, offering a rapid and cost-effective alternative for residential construction.
2. Infrastructure Projects: Large-scale 3D printing is employed for constructing bridges, tunnels, and other infrastructure elements, showcasing its potential for shaping the future of civil engineering.
3. Commercial Buildings: From office complexes to retail spaces, 3D printing is utilized to create unique architectural designs efficiently and with reduced construction timelines.
4. Customized Structures: The technology allows for the creation of customized structures, catering to specific design requirements and individual preferences.
5. Emergency and Disaster Relief: 3D printing enables the quick construction of temporary shelters and emergency housing in disaster-stricken areas, providing a rapid response to urgent housing needs.
6. Monumental Structures: The construction of large and intricate sculptures or monuments is facilitated by 3D printing, allowing for precise and detailed designs.
7. Renovation and Restoration: 3D printing is used to recreate historical or damaged architectural elements, allowing for the restoration of buildings and monuments with accuracy.
8. Educational Structures: Schools and educational institutions leverage 3D printing for constructing innovative and modern learning spaces, showcasing its application in the educational sector.
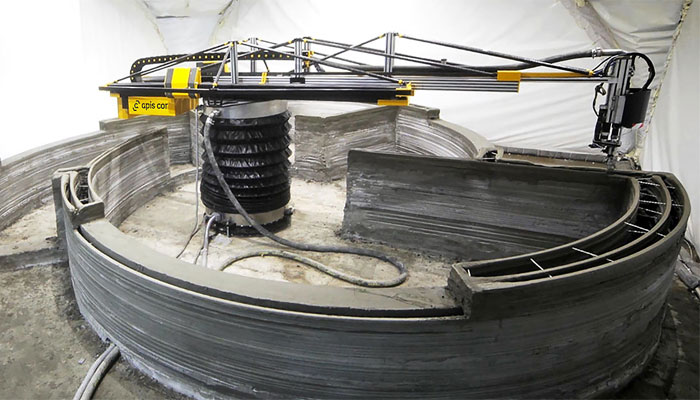

The growing adoption of 3d printing technology for construction in India
The increasing demand for 3D printing technology in India is notably driven by a confluence of factors contributing to its growth and adoption across various sectors. Industries such as healthcare, aerospace, automotive, and manufacturing are witnessing a surge in interest due to the technology's ability to offer rapid prototyping, cost-effective production, and customization. The healthcare sector, in particular, has embraced 3D printing for medical applications like patient-specific implants and prosthetics. Additionally, the government's initiatives promoting innovation, coupled with a growing number of startups in the 3D printing domain, have spurred awareness and integration of this technology. As businesses recognize its potential to enhance efficiency and reduce production costs, the demand for 3D printing in India is poised for continued growth, reflecting a broader trend toward advanced manufacturing solutions in the country. Recently, India's First 3D-Printed Post Office Inaugurated in Bengaluru.
India's First 3D-Printed Post Office
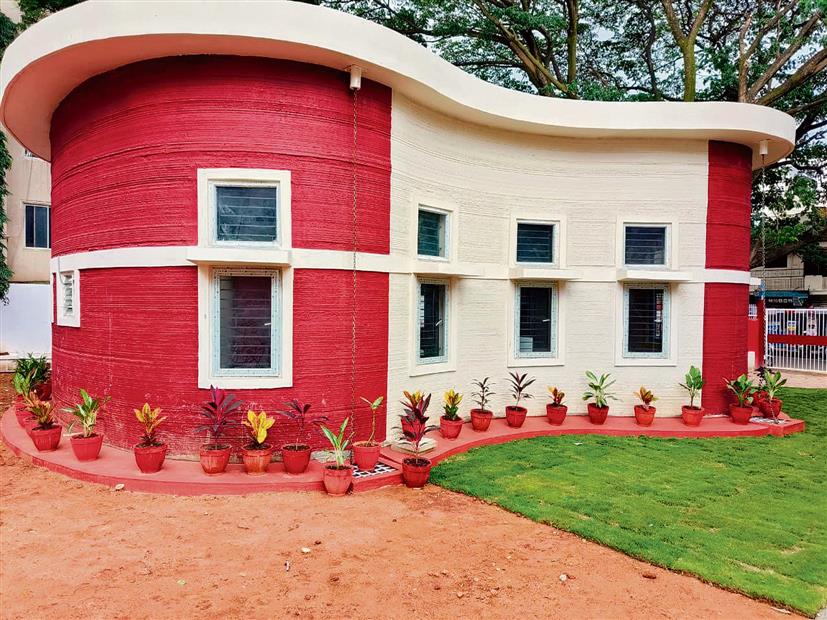

This technological marvel, constructed by Larsen & Toubro Limited with technological support from IIT Madras under the guidance of Professor Manu Santhanam, represents a remarkable feat in modern construction. Completed in an impressive 43 days, two days ahead of schedule, the project underscores the efficiency and speed afforded by 3D printing technology in creating essential public infrastructure. The collaborative effort between a multinational corporation and a renowned academic institution highlights the potential for global partnerships in advancing innovative construction practices.
To execute 3D printing, the process is remarkably streamlined – a personal computer connected to a 3D printer is all that's required. Utilizing computer-aided design (CAD) software, one designs a 3D model of the desired object and initiates the 'print' command. The 3D printer then takes charge, seamlessly translating the digital design into a tangible structure. This achievement not only signifies a major leap in construction efficiency but also serves as a beacon for the integration of cutting-edge technology in shaping the future of public services.
Market potential of 3d technology in construction
As per straits research report, The global 3D printing construction market size was worth USD 1.094 billion in 2021. It is expected to reach USD 585.84 billion by 2030, growing at an impressive CAGR during the forecast period (2022–2030).
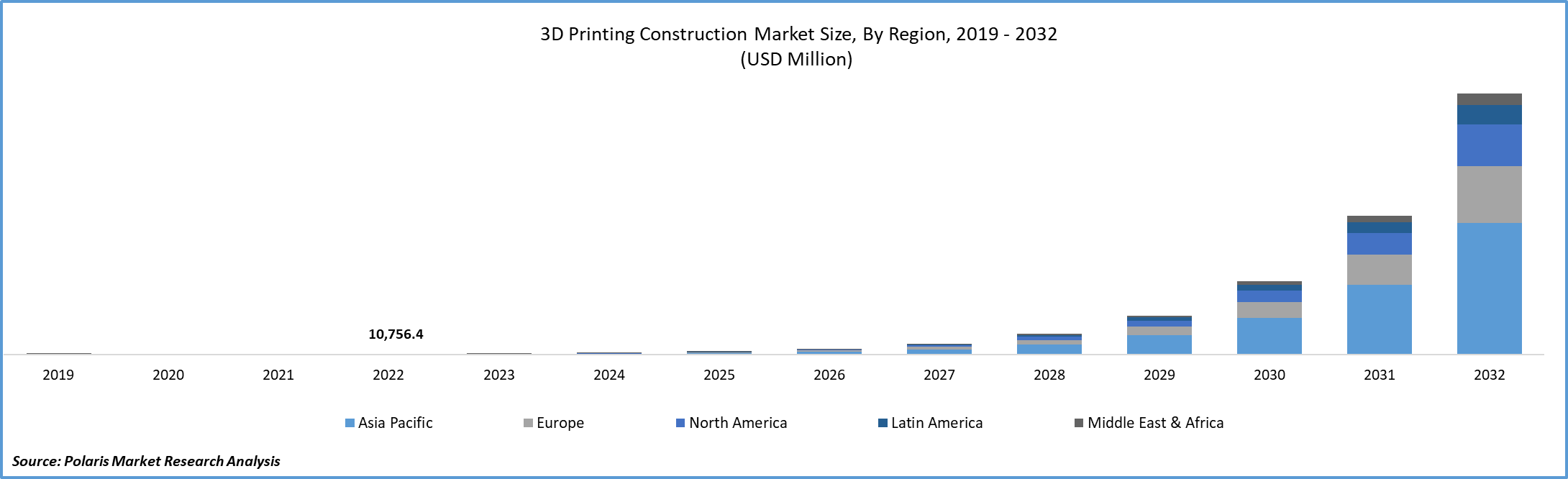
As per Polaris Market Research report, The global 3D printing construction market was valued at USD 10,756.4 thousand in 2022 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 88.3% during the 2023- 2032 period. The 3D printing construction market has witnessed significant growth in recent years and is expected to continue expanding rapidly. Compared to traditional building methods, 3D printing construction offers numerous advantages, including time and effort savings, accelerated infrastructure development, waste reduction, and improved safety by minimizing the risk of injuries. These factors will drive the industry's growth in the coming years.
The adoption of Building Information Modeling (BIM) is a key driver behind the growth of the 3D Printing Construction industry. BIM is the cornerstone of digital transformation in architecture, engineering, and infrastructure. It enables seamless collaboration among various professionals, including architects, real estate developers, engineers, manufacturers, contractors, and others involved in the construction process. BIM allows stakeholders to plan, design, and visualize structures or buildings in a unified 3D environment.
The Predominance of Asia-Pacific in the Regional Market
Asia-Pacific holds the largest share of the global 3D printing construction market. Asia-Pacific controls the majority of the global 3D printing construction industry. The 3D Printing technology is expected to gain significant traction during the forecast period as the region establishes itself as a global manufacturing hub. The presence of many manufacturing sectors contributes to the region's overall economic growth.
Due to the existence of several manufacturers, the region is an important market for 3D printing construction. The growing demand for 3D printing construction in the building and infrastructure end-use sectors is also going to fuel the development of the market. China and Southeast Asia dominate the APAC 3D printing construction market. Since this evolving technology is yet to be commercialized in India, South Korea, Japan, and other Asian countries, they have been classified as the rest of APAC. Research activities in Japan and India, on the other side, make these prospective countries markets for this technology.
According to a new report published by XResearch, titled, “India 3D printing Market Insights, Trends, Opportunity & Forecast, 2023–2030,” the India 3D printing market size is anticipated to witness moderate growth during the forecast period i.e., 2023-2030.The India 3D printing market is anticipated to grow at a high CAGR of 20.3% from 2023 to 2030. The market's revenue surged to $111.0 million in 2022, and it is expected to further accelerate, reaching a notable $705.1 million by 2030.
Future Scope
The 3D printing technology in the construction industry is in its developmental phase and we are already seeing many individual small-scale residential projects and demo buildings coming up which are showcasing its potential and benefits. Since the construction industry is very complex and crowded with multiple stakeholders working on site simultaneously, the intervention of 3D printing technology simplifies a lot of things and streamlines the process, thereby achieving more efficiency and reducing the chances of error. Over time, we will experience challenges with the adoption of this technology like any other technology that has come up in the past, but they will be mitigated and soon 3D printing will dominate the way construction is being done. There have already been talks about using similar technology for space missions and it would be very interesting to see the limits and potential of this technological advancement
Conclusion
3D printing technology has emerged as a transformative force in the construction industry, ushering in an era of unparalleled innovation and efficiency. The ability to construct intricate designs with precision, reduce material waste, and accelerate project timelines marks a significant paradigm shift. As demonstrated by pioneering projects globally and the nascent initiatives in India, 3D printing has the potential to revolutionize traditional construction methods. The technology not only offers sustainable solutions but also opens avenues for architectural creativity and cost-effective construction. While challenges like scalability and material advancements persist, the trajectory of 3D printing in construction points towards a future where buildings are not just erected but intricately crafted, offering a glimpse into a more sustainable and architecturally diverse tomorrow. As the industry continues to embrace this cutting-edge technology, the construction landscape stands on the brink of a radical transformation, fueled by the layers of innovation that 3D printing brings to the very foundation of our built environment.
Cover image- getpowerplay.in









.png)