The construction industry is increasingly focused on sustainable solutions to meet the growing demands for energy efficiency and environmental impact reduction. One of the most promising innovations in this field is transparent wood—a material that combines the benefits of traditional wood with advanced technology to offer a new dimension in construction.
Introduction to Transparent Wood
Transparent wood was first developed by German researcher Siegfried Fink in 1992. However, it wasn't until 2015-2016 that significant advancements were made by Professor Lars Berglund from KTH Royal Institute of Technology in Sweden and Professor Liang Bing Hu from the University of Maryland. They improved the process by removing lignin and adding polymers to achieve greater transparency and functionality in the material.
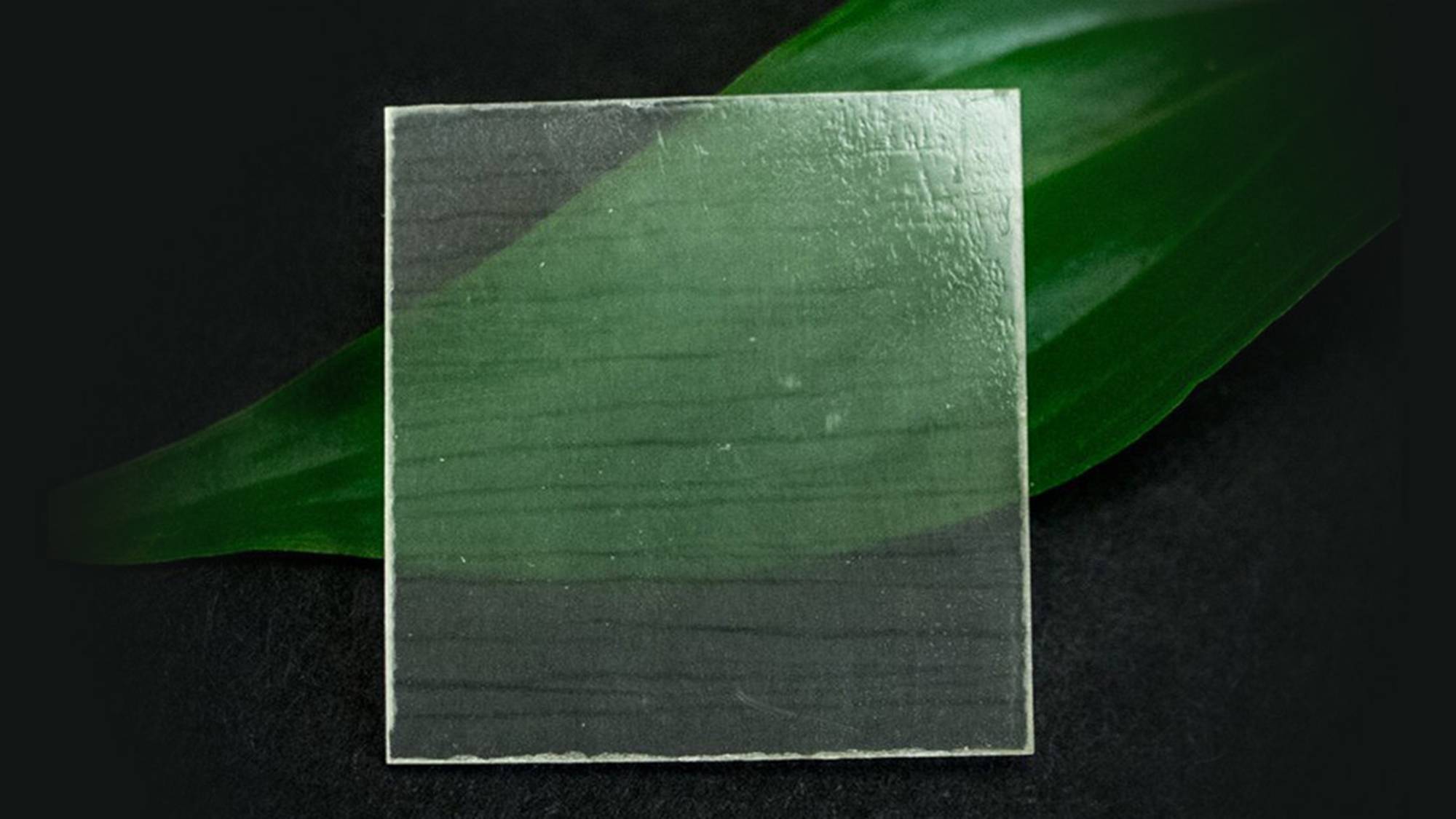
Transparent wood represents a significant advancement in building materials, merging the natural benefits of wood with innovative processing techniques. Traditionally, wood has been prized for its excellent insulation properties and aesthetic appeal. However, its opacity and susceptibility to environmental factors have limited its applications. Transparent wood, a material that allows light to pass through while retaining the structural benefits of wood, offers an exciting alternative for sustainable architecture.
The Science Behind Transparent Wood
Wood is inherently opaque due to its lignin content, which absorbs light and gives wood its characteristic color. To create transparent wood, researchers employ a sophisticated process to remove lignin and fill the wood’s porous structure with a transparent polymer. The result is a material that retains the structural integrity of wood while achieving a level of transparency.
The process begins by treating wood with chemicals to remove lignin. This treatment usually involves a combination of sodium hydroxide and sodium sulfite. The treated wood, now free of lignin, is bleached further with hydrogen peroxide. The next step involves infiltrating the wood with a polymer resin, such as polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), under vacuum conditions. This resin fills the wood’s pores and binds the structure, creating a transparent material that retains the natural grain and texture of wood.
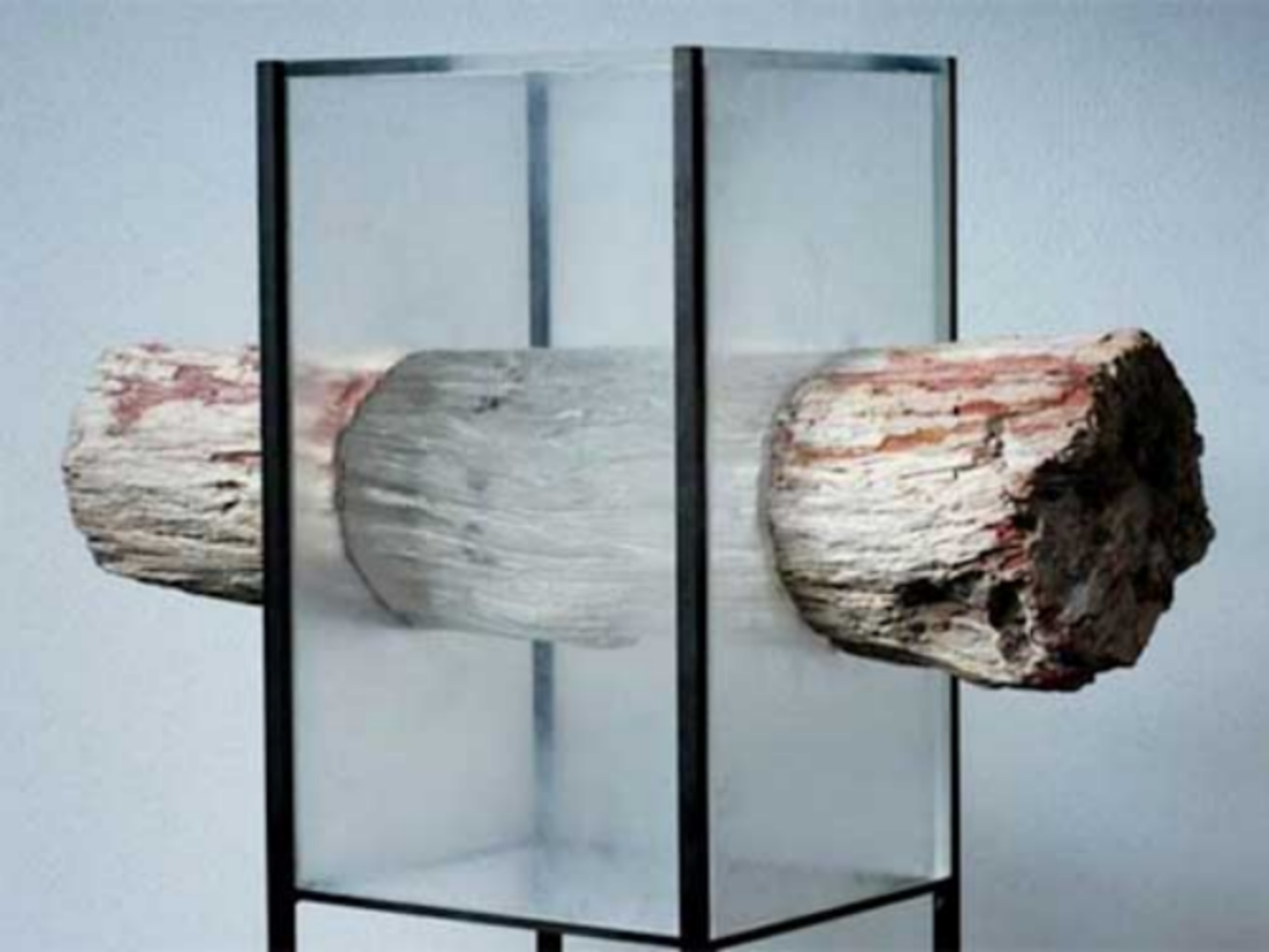

Properties of Transparent Wood
Transparent wood exhibits several enhanced properties compared to traditional wood. Its mechanical strength is significantly improved, making it ten times more stress-resistant and four times more strain-resistant than conventional wood. The material's mechanical properties are influenced by the cellulose content and the orientation of the wood fibers. Additionally, transparent wood has a low thermal conductivity, which contributes to its effectiveness as an insulator.
One of the key benefits of transparent wood is its ability to store and release heat. By incorporating phase change materials (PCMs) like polyethylene glycol, transparent wood can absorb and store heat when temperatures rise and release it when temperatures fall. This characteristic enhances the material’s suitability for energy-efficient building designs.
Advantages of Transparent Wood
1. Enhanced Aesthetic Appeal: Transparent wood combines the natural beauty of traditional wood with a modern, sleek appearance, creating a unique material that can enhance both architectural and interior design.
2. Improved Mechanical Strength: Compared to conventional wood, transparent wood exhibits significantly greater mechanical strength. It is ten times more stress-resistant and four times more strain-resistant, making it suitable for demanding applications.
3. Superior Thermal Insulation: With low thermal conductivity, transparent wood offers excellent insulation properties. It can effectively reduce heat loss and gain, contributing to energy-efficient building designs.
4. Light Transmission and Diffusion: The material allows natural light to pass through while diffusing it evenly. This can reduce the need for artificial lighting, leading to energy savings and improved interior lighting conditions.
5. Heat Storage and Release: Transparent wood can incorporate phase change materials (PCMs), which absorb, store, and release heat. This feature enhances its energy efficiency and thermal regulation capabilities.
6. Sustainable and Renewable: Transparent wood is derived from a renewable resource—wood. With advancements in processing, it offers a sustainable alternative to conventional building materials.
7. Reduction of Carbon Footprint: As a sustainable material, transparent wood can contribute to lowering the carbon footprint of construction projects, aligning with global efforts to reduce environmental impact.
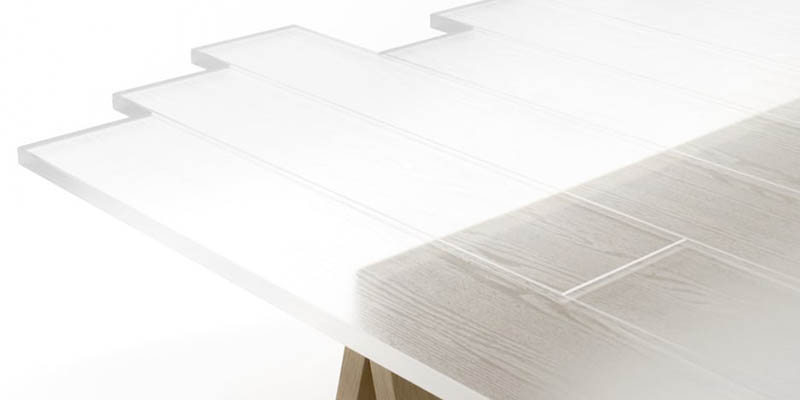

Applications of Transparent Wood
Transparent wood holds promise for a variety of applications in architecture and design. Its unique combination of transparency, strength, and insulation properties makes it suitable for several innovative uses:
1. Architectural Facades and Roofing: Transparent wood can be used in building facades and roofs to enhance natural light entry while maintaining privacy. Its ability to diffuse light evenly can reduce the need for artificial lighting, contributing to energy savings in buildings.
2. Energy-Efficient Windows: Transparent wood’s mechanical strength and insulation properties make it a viable option for high-performance windows. These windows can offer improved thermal insulation and durability compared to traditional glass, potentially leading to more energy-efficient buildings.
3. Smart Building Elements: Functionalized transparent wood can be incorporated into smart building designs. By integrating quantum dots or magnetic nanoparticles, the material can achieve properties such as luminescence or electromagnetic shielding, opening up new possibilities for advanced building technologies.
4. Furniture and Interior Design: Transparent wood’s aesthetic appeal and durability make it an attractive material for furniture and interior design elements. Its unique appearance and strength allow for the creation of visually striking and functional pieces.
Market Potential of Transparent Wood
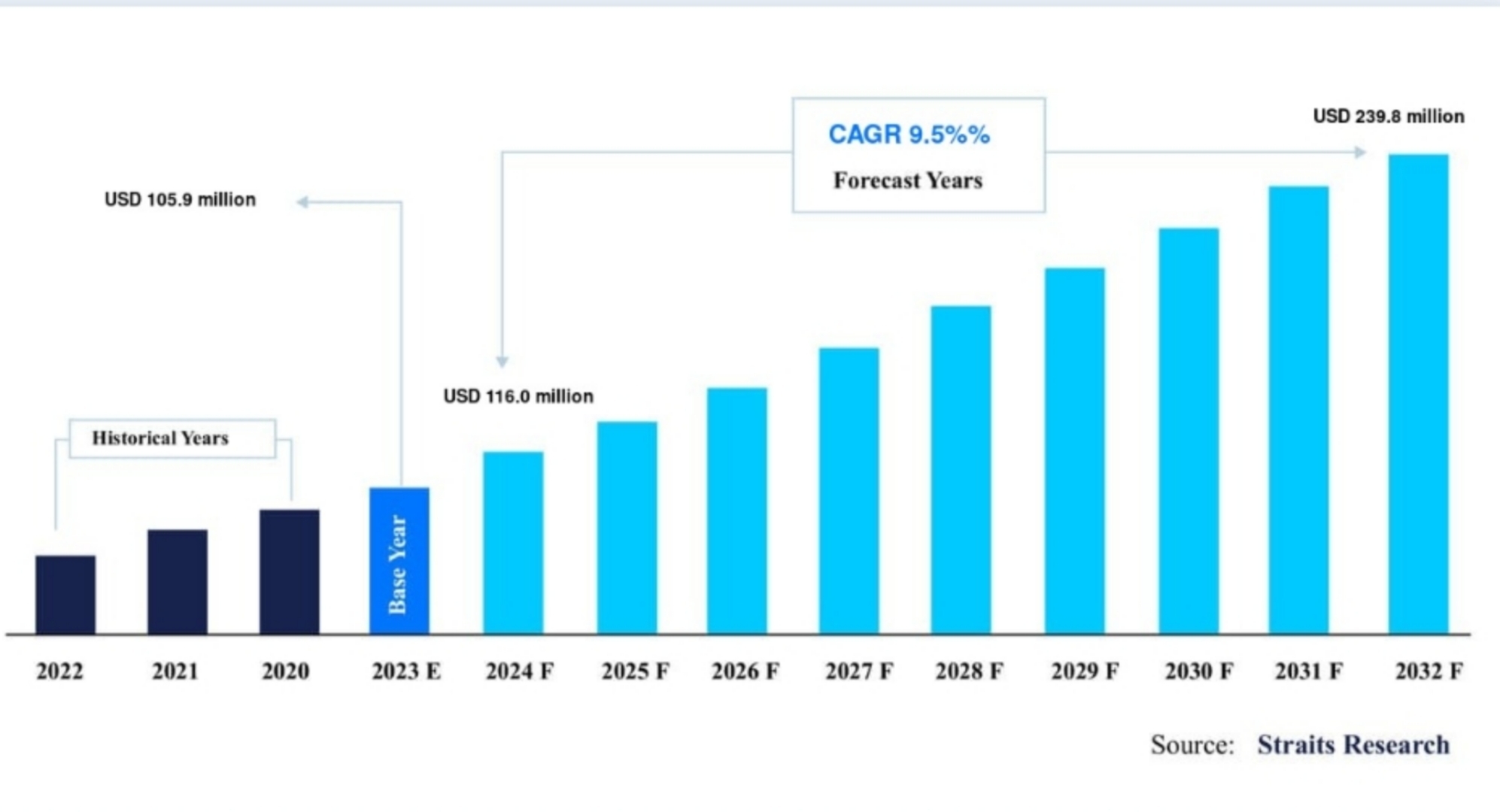
As per Straits Research report, the global transparent wood market size was valued at USD 105.9 million in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 239.8 million by 2032, registering a CAGR of 9.5% during the forecast period (2024–2022). The increased usage of transparent wood in various applications, including building, furniture, solar cells, automobile windshields, see-through packaging, and others, is anticipated to be a key growth driver for the global transparent wood market.
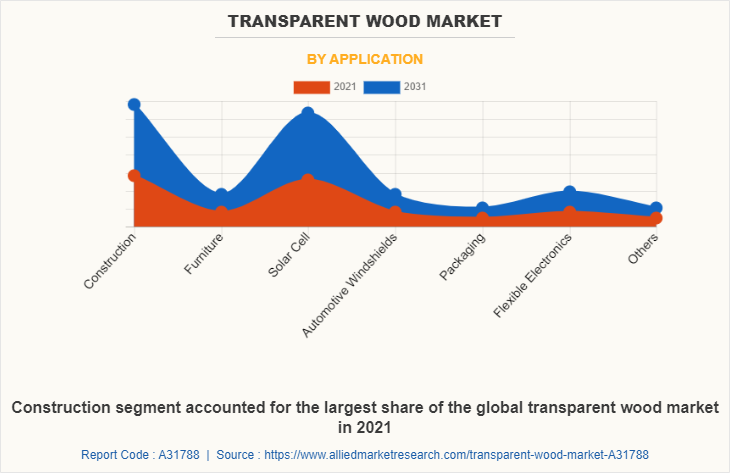
As per Allied Market Research, the global transparent wood market was valued at $88.4 million in 2021 and is projected to reach $208.1 million by 2031. This growth represents a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9.0% from 2022 to 2031. This expansion highlights the increasing interest and investment in transparent wood as a sustainable and innovative building material.
Challenges and Future Outlook
Despite its advantages, transparent wood faces several challenges that need to be addressed for widespread adoption. One major issue is the environmental impact of the epoxy resins used in the manufacturing process. While current production methods rely on non-recyclable materials, ongoing research aims to develop more sustainable alternatives.
Another challenge is scaling up the production of transparent wood. While small samples have been successfully created in laboratory settings, producing large-scale panels and components remains a technical hurdle. Advances in manufacturing techniques and material science are essential to make transparent wood a practical and commercially viable option.
Conclusion
Transparent wood represents a significant advancement in construction materials, offering a blend of natural wood aesthetics and modern technological benefits. Its superior mechanical properties, thermal insulation capabilities, and innovative applications make it a promising candidate for future architectural and design projects. As research and development continue to address the challenges associated with its production and environmental impact, transparent wood is poised to become a key player in sustainable building practices. With its potential to revolutionize the way we think about construction materials, transparent wood stands as a testament to the exciting possibilities at the intersection of nature and technology.
Image sources- knowablemagazine.org, architectureanddesign.com, archivibe.com








.png)