Computer-Aided Design (CAD) is a software that empowers architects, engineers, and designers to conceptualize, visualize, and refine building plans with unparalleled precision and efficiency. By harnessing cutting-edge software, CAD facilitates the creation of detailed 2D and 3D models, enabling stakeholders to explore every facet of a project before its execution. From intricate structural details to spatial arrangements, CAD empowers teams to iterate rapidly, analyze designs for potential issues, and make informed decisions that optimize functionality, aesthetics, and sustainability. Seamless integration with other software platforms and collaboration tools fosters communication and coordination across disciplines, ensuring seamless project execution from concept to completion. With CAD, the construction industry transcends traditional limitations, embracing innovation and pushing the boundaries of what's possible in architectural design and engineering.
Advantages of Computer-Aided Design (CAD) for Construction
2. Improved Accuracy: One of the primary benefits of CAD is its ability to create highly accurate and detailed designs. Traditional hand-drawn methods are prone to human error, but CAD software ensures precision by using exact measurements and providing tools for aligning, snapping, and scaling elements correctly. This accuracy is crucial for ensuring that parts fit together perfectly in the final product, which is especially important in fields like aerospace, automotive, and manufacturing where tolerances are very tight.
3. Enhanced Visualization: CAD software allows designers to create detailed 3D models and realistic renderings of their projects. These visualizations help in understanding the spatial relationships and aesthetics of the design, which can be crucial for stakeholders who may not be familiar with technical drawings. High-quality visualizations facilitate better communication and can be used for presentations and marketing materials, making it easier to gain client approvals and investor support.
4. Easy Modifications: The ability to quickly and easily modify designs is a key advantage of CAD. Designers can make changes to a model with just a few clicks, without the need to start from scratch. This flexibility is invaluable when responding to new information, client feedback, or changing project requirements. It also allows for the exploration of multiple design alternatives, leading to more refined and optimized solutions.
5. Better Documentation: CAD software generates comprehensive and standardized documentation that is essential for the manufacturing and construction phases of a project. This documentation includes detailed drawings, specifications, material lists, and assembly instructions. Having accurate and complete documentation reduces the risk of errors during production and ensures that everyone involved in the project has access to the same information, thereby improving coordination and efficiency.
6. Simulation and Analysis: Many CAD tools come equipped with simulation features that allow designers to test how their designs will perform under various conditions. This can include structural analysis, thermal analysis, fluid dynamics, and more. By simulating real-world conditions, designers can identify potential issues and optimize their designs before any physical prototypes are made. This not only saves time and resources but also enhances the reliability and performance of the final product.
7. Collaboration: Modern CAD software supports collaborative work environments where multiple designers can work on the same project simultaneously. Cloud-based CAD platforms enable real-time collaboration, allowing team members from different locations to share updates, provide feedback, and make changes in real-time. This collaborative approach enhances communication, reduces the likelihood of conflicts, and ensures that everyone is on the same page, ultimately leading to a more cohesive and efficient design process.
8. Cost Savings: By reducing the need for physical prototypes and minimizing design errors, CAD helps lower overall project costs. The ability to quickly iterate and optimize designs means that fewer materials are wasted and less time is spent on rework. Additionally, the improved accuracy and detailed documentation provided by CAD reduce the likelihood of costly mistakes during production. These cost savings can be significant, especially in large-scale projects or in industries where precision and quality are paramount.
9. Integration with Other Systems: CAD software often integrates seamlessly with other tools used in the product development process, such as Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems. This integration ensures a smooth transition from design to production, enabling efficient planning, scheduling, and resource management. It also allows for better data management and traceability throughout the product lifecycle, enhancing overall project coordination and execution.

Types of Computer-Aided Design (CAD) used in construction
1. 2D CAD: Two-dimensional CAD software remains a cornerstone in construction design due to its precision and versatility. These tools are fundamental for drafting detailed architectural drawings that include floor plans, elevations, and cross-sections. They allow designers to specify every detail, from room dimensions and wall placements to the layout of doors and windows. 2D CAD is also critical for creating technical documents like site plans, which map out the placement of buildings on a plot of land, including landscaping and utilities. The ability to layer information helps manage complex designs by separating different elements, such as electrical layouts from plumbing schematics, ensuring clarity and ease of updates.
2. 3D CAD: Three-dimensional CAD software transforms the way designers visualize and communicate their ideas. By constructing detailed 3D models, these tools provide a more immersive experience that helps stakeholders understand the spatial relationships and aesthetics of a design. 3D CAD allows for virtual walkthroughs, which can reveal potential design flaws or spatial conflicts that might not be apparent in 2D drawings. Additionally, these models can be used to perform volumetric analyses and daylight simulations, helping to optimize the design for energy efficiency and occupant comfort. The ability to easily adjust and refine these models makes 3D CAD indispensable for iterative design processes and client presentations.
3. Building Information Modeling (BIM): BIM software goes beyond simple 3D modeling by integrating detailed data about each building component. This information-rich approach allows for comprehensive project management, from initial design through construction and into facility management. BIM models include data on materials, specifications, and maintenance schedules, providing a single source of truth that enhances collaboration among all stakeholders. BIM facilitates clash detection, identifying conflicts between systems (e.g., plumbing and electrical) early in the design phase, thus preventing costly on-site modifications. By simulating construction processes, BIM helps in planning logistics, sequencing tasks, and ensuring compliance with building codes and regulations.
4. Structural CAD: Structural CAD software are used for designing and analyzing the structural integrity of buildings. These programs allow engineers to model various structural elements such as beams, columns, trusses, and foundations, considering factors like load-bearing capacity, material strength, and safety standards. They perform complex calculations to simulate how structures will respond to stresses such as wind, earthquakes, and heavy loads. Structural CAD also supports the design of reinforcement in concrete structures, ensuring that they can withstand expected forces without failure. This precision helps in optimizing material usage, reducing costs, and ensuring that structures meet all safety and performance criteria.
5. Civil CAD: Civil CAD software is essential for infrastructure projects like roads, bridges, and drainage systems. These tools enable civil engineers to design detailed alignments, profiles, and cross-sections for transportation networks. Civil CAD supports the analysis of topography, soil stability, and hydrology, ensuring that designs are both feasible and sustainable. The software's grading and earthwork capabilities allow for precise calculations of cut-and-fill volumes, which are critical for project planning and cost estimation. By integrating geospatial data, Civil CAD helps create accurate site models and maps, facilitating better planning and decision-making in large-scale infrastructure projects.
6. Electrical CAD: Electrical CAD are used to create comprehensive electrical system designs. These tools support the drafting of detailed schematics, wiring diagrams, and control panel layouts. They provide libraries of standard electrical components and symbols, ensuring consistency and compliance with industry standards. Electrical CAD software also includes features for conducting load calculations, voltage drop analysis, and circuit protection design. This ensures that electrical systems are safe, efficient, and capable of meeting the power requirements of modern buildings. The ability to simulate electrical circuits helps in identifying potential issues before installation, reducing the risk of costly rework.
7. Mechanical CAD: Mechanical CAD is crucial for the design and integration of HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) systems, plumbing, and other mechanical systems in buildings. These tools enable the creation of detailed 3D models that show how mechanical components fit within the overall building design. Mechanical CAD allows for the simulation of airflow, thermal performance, and energy consumption, helping to optimize systems for efficiency and comfort. It also supports the design of complex piping and ductwork systems, ensuring they are properly sized and routed. The ability to coordinate mechanical systems with architectural and structural elements minimizes conflicts and facilitates smoother installations.
8. Landscape CAD: Landscape CAD software is used for the design and planning of outdoor spaces. These tools enable landscape architects to create detailed site plans that include elements like terrain contours, plantings, water features, and hardscapes. Landscape CAD supports the analysis of environmental factors, such as soil conditions, drainage patterns, and sunlight exposure, ensuring that designs are sustainable and suited to the local ecosystem. The software can generate planting schedules, irrigation plans, and construction details, helping to streamline project implementation. By visualizing the landscape in 3D, designers can better communicate their vision and make informed decisions about aesthetics and functionality.
Applications of Computer-Aided Design (CAD) in construction
1. Architectural Design: CAD is integral to the architectural design process, allowing architects to create detailed 2D and 3D models of buildings. These models provide a comprehensive view of the proposed structure, including floor plans, elevations, sections, and detailed construction drawings. CAD software enables architects to experiment with different design concepts and visualize the final outcome, making it easier to communicate ideas to clients and stakeholders. It also supports the integration of various building components, ensuring a cohesive and well-coordinated design.
2. Structural Engineering: In structural engineering, CAD is used to design and analyze the structural elements of buildings and infrastructure. Software like STAAD.Pro and SAP2000 allows engineers to model beams, columns, trusses, and foundations, and to simulate how these elements will behave under various loads and conditions. This ensures that structures are safe, stable, and compliant with building codes. CAD also helps optimize material usage, reducing costs and environmental impact while maintaining structural integrity.
3. Mechanical, Electrical, and Plumbing (MEP) Design: CAD applications in MEP design involve the detailed planning and coordination of mechanical, electrical, and plumbing systems within a building. Tools like Revit MEP and AutoCAD MEP enable engineers to create precise 3D models of HVAC systems, electrical wiring, and plumbing networks. These models ensure that all systems are properly integrated and do not interfere with each other or the architectural and structural elements. CAD also facilitates load calculations, energy analysis, and system optimization, leading to more efficient and sustainable building operations.
4. Building Information Modeling (BIM): BIM is a sophisticated application of CAD that integrates 3D modeling with information management throughout the building lifecycle. BIM software like Revit and ArchiCAD enables the creation of detailed models that include data on materials, specifications, and performance characteristics. This comprehensive approach enhances collaboration among architects, engineers, contractors, and facility managers, ensuring that everyone has access to up-to-date information. BIM supports clash detection, construction scheduling, and lifecycle management, improving project coordination, reducing errors, and increasing overall efficiency.
5. Site and Civil Engineering: In site and civil engineering, CAD is used for designing and planning infrastructure projects such as roads, bridges, and drainage systems. Civil CAD software like Civil 3D and MicroStation allows engineers to create detailed alignments, profiles, and cross-sections. These tools facilitate the analysis of topography, soil stability, and hydrology, ensuring that designs are both feasible and sustainable. CAD also supports the integration of geospatial data, enabling accurate site modeling and mapping, which is crucial for large-scale infrastructure projects.
6. Construction Documentation: CAD plays a crucial role in generating construction documentation, including detailed drawings, specifications, and material lists. These documents are essential for guiding construction activities and ensuring that all project requirements are met. CAD software allows for the creation of precise and standardized documentation that can be easily updated and shared among project stakeholders. This improves communication, reduces the likelihood of errors, and ensures that all parties have access to the same information.
7. Project Visualization and Presentation: CAD enhances project visualization and presentation by producing high-quality renderings and animations. These visualizations provide a realistic view of the proposed building or infrastructure, making it easier for stakeholders to understand and approve the design. Tools like SketchUp and Rhino enable the creation of virtual walkthroughs and flyovers, which are valuable for marketing, client presentations, and public consultations. This ability to visualize the final outcome helps build confidence and support for the project.
8. Construction Planning and Management: CAD aids in construction planning and management by facilitating the detailed scheduling and sequencing of construction activities. BIM software, in particular, allows for the simulation of construction processes, helping to identify potential issues and optimize workflows. This ensures that projects are completed on time and within budget. CAD also supports the management of resources, including labor, materials, and equipment, improving overall project efficiency and reducing costs.
9. Sustainability and Environmental Analysis: CAD is increasingly used to support sustainability and environmental analysis in construction projects. Tools like Green Building Studio and Sefaira enable the assessment of energy performance, daylighting, and thermal comfort, helping designers create more sustainable buildings. These tools allow for the simulation of various design scenarios, facilitating the selection of materials and systems that minimize environmental impact. CAD also supports the integration of renewable energy sources and the implementation of green building standards, contributing to the development of environmentally responsible projects.
Market Potential of Computer-Aided Design (CAD) in India
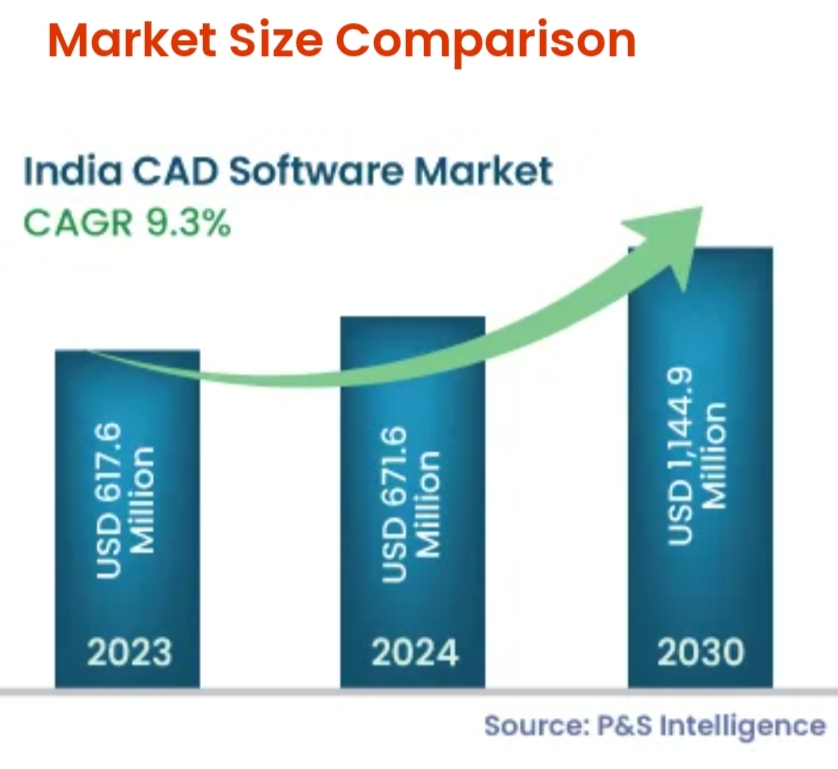
As per Prescient Strategic Intelligence, The projected growth of the Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software market in India, expected to reach $1,144.9 million with a CAGR of 9.3% from 2024–2030.
As per Statista report, The Construction and Design market in India is poised for significant growth, with revenue projected to reach US$148.30 million by 2024. This growth trajectory is expected to continue steadily, with an annual growth rate (CAGR 2024-2028) of 7.55%. By 2028, the market volume is forecasted to expand to US$198.40 million.
Conclusion
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) has revolutionized the construction industry by significantly enhancing design precision, efficiency, and collaboration. As discussed, CAD software enables architects, engineers, and contractors to create detailed 2D and 3D models that facilitate better visualization, analysis, and communication throughout the project lifecycle. This technological advancement not only accelerates project timelines and reduces costs but also improves overall project outcomes by minimizing errors and optimizing resource utilization. Looking ahead, as CAD continues to evolve with advancements in automation, artificial intelligence, and cloud computing, its role in shaping the future of sustainable, smart, and efficient construction practices in India and globally will undoubtedly remain pivotal.
Image sources- wconline.com,homedesigninstitute.com, thebirmgroup.com









.png)