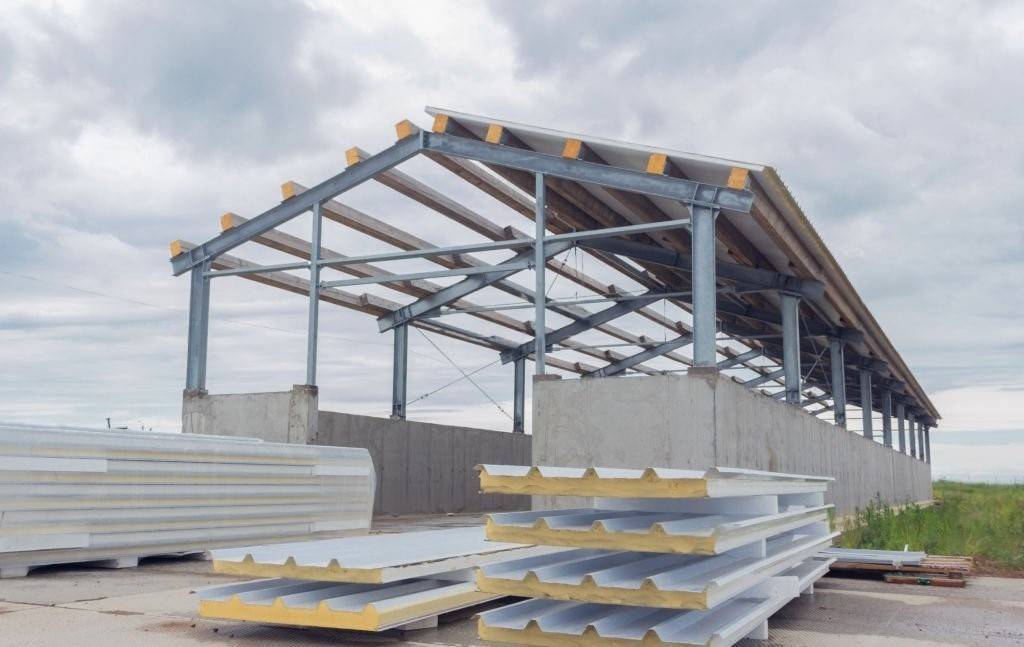
Prefabrication refers to the process of constructing components or entire buildings off-site in a controlled environment, such as a factory or manufacturing facility, before transporting them to the final construction site for assembly. This method allows for greater efficiency, quality control, and cost-effectiveness compared to traditional on-site construction methods. Prefabricated components can include walls, floors, roofs, and even entire modules or sections of buildings.
The prefabrication method typically involves several key steps:
1. Design: Architects and engineers create detailed plans for the building or components to be prefabricated, taking into account the specific requirements of the project and any applicable building codes or regulations.
2. Fabrication: Components are manufactured off-site in a factory or workshop. This may involve cutting, shaping, assembling, and finishing various materials such as steel, concrete, wood, or composite materials according to the design specifications.
3. Quality Control: During fabrication, rigorous quality control measures are implemented to ensure that each component meets the required standards for strength, durability, and precision. This includes inspections, testing, and monitoring of materials and production processes.
4. Transportation: Once fabricated, the components are transported to the final construction site. This may involve shipping by truck, rail, or even by sea, depending on the size and location of the components and the project site.
5. Assembly: On-site, the prefabricated components are assembled according to the construction plans. This process may involve lifting, positioning, and connecting the components using cranes, lifting equipment, and specialized techniques.
6. Integration: Prefabricated components are integrated with other building elements, such as foundations, utilities, and finishes, to complete the construction of the building or structure.
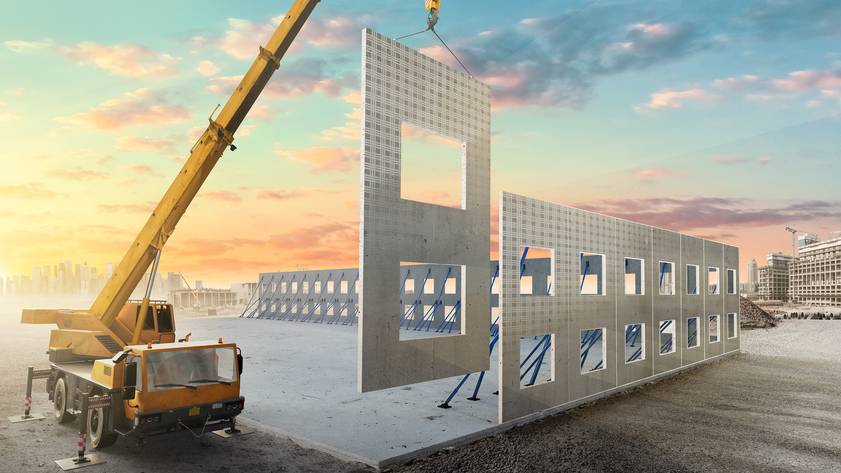

Advantages of prefabrication construction
1. Efficiency: Prefabricated components are manufactured in controlled environments, allowing for efficient production processes and reducing construction time on-site.
2. Cost-effectiveness: Prefabrication can lead to cost savings through reduced labor costs, shorter construction schedules, minimized material waste, and better cost predictability due to controlled manufacturing processes.
3. Quality control: Factory-controlled production ensures consistent quality of prefabricated components, resulting in higher quality buildings with fewer defects.
4. Safety: By moving construction activities off-site, prefabrication can improve safety conditions for workers by minimizing exposure to hazardous on-site conditions and reducing the risk of accidents.
5. Sustainability: Prefabrication can be more environmentally friendly than traditional construction methods, as it often generates less waste, consumes fewer resources, and allows for greater control over energy efficiency and sustainable building practices.
6. Flexibility and customization: Prefabricated components can be tailored to meet specific project requirements, offering flexibility in design and customization options while still benefiting from the efficiencies of off-site manufacturing.
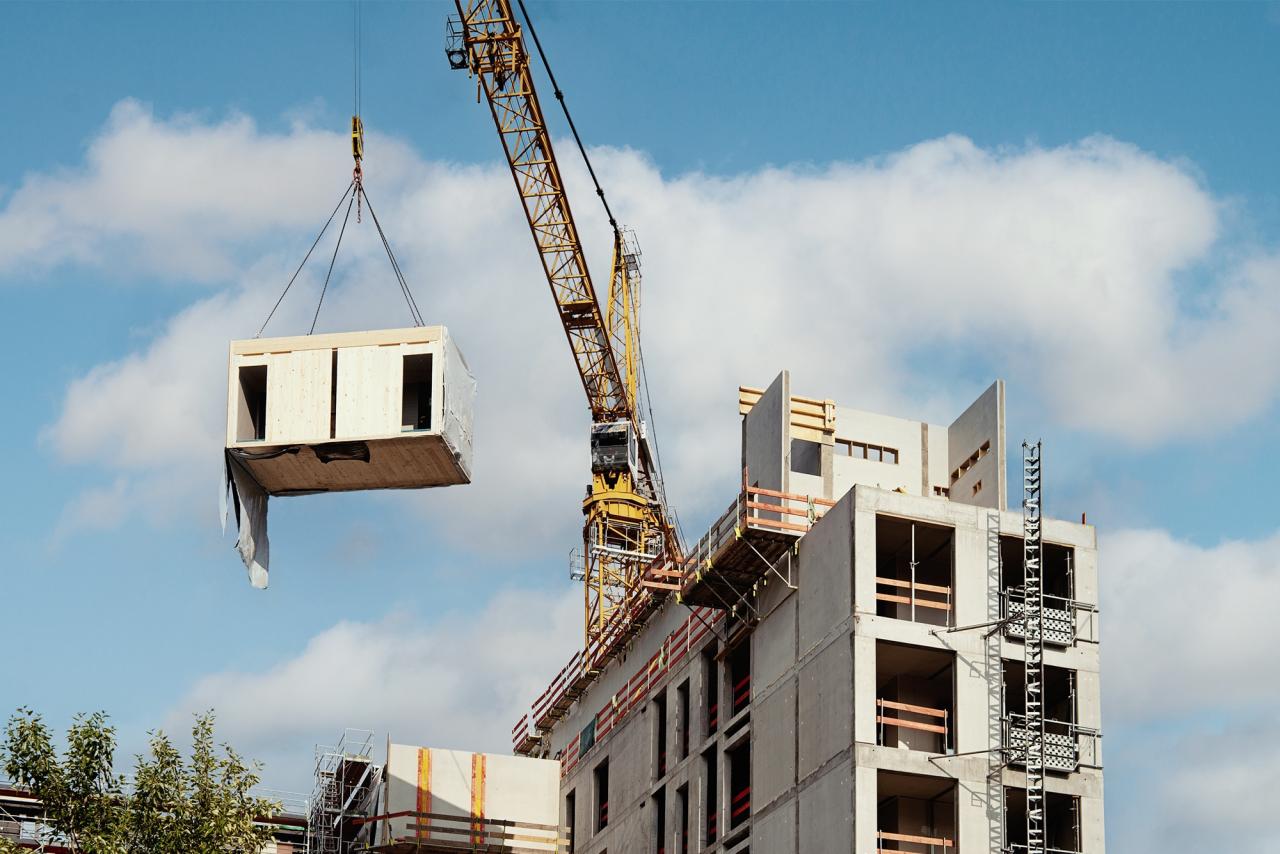

Types of prefabrication construction
Prefabrication encompasses various types, each offering unique advantages and applications. Here are some common types of prefabrication:
1. Modular Construction: Modular construction involves manufacturing building modules or sections off-site in a factory-controlled environment. These modules are then transported to the construction site for assembly into the final structure. Modular construction is highly customizable, offers fast construction timelines, and is suitable for a wide range of building types, including residential, commercial, and institutional.
2. Panelized Construction: Panelized construction involves prefabricating building panels, such as walls, floors, and roofs, off-site and then transporting them to the construction site for assembly. Panelized construction offers flexibility in design, faster construction times, and improved quality control.
3. Prefabricated Components: Prefabricated components include individual building elements, such as columns, beams, stairs, and façade elements, that are manufactured off-site and then integrated into the construction process. Prefabricated components can be customized to meet specific project requirements and offer efficiency in construction.
4. Volumetric Construction: Volumetric construction, also known as modular or off-site volumetric construction, involves manufacturing entire building modules or units off-site, including complete rooms or sections of buildings. These volumetric units are then transported to the construction site and assembled to form the final structure. Volumetric construction offers speed, quality, and consistency in construction and is often used for residential, hospitality, and student housing projects.
5. Prefabricated Facades: Prefabricated facades are pre-assembled building envelope components, such as curtain walls, cladding panels, and window systems, that are manufactured off-site and then installed onto the building's structure. Prefabricated facades offer design flexibility, improved thermal performance, and reduced on-site construction time.
6. Prefabricated MEP Systems: Prefabricated mechanical, electrical, and plumbing (MEP) systems involve manufacturing building services components, such as HVAC ducts, piping, and electrical panels, off-site and then installing them into the building during construction. Prefabricated MEP systems reduce on-site labour and coordination, improve installation quality, and accelerate construction schedules.

Applications of prefabrication construction in real estate
1. Residential Construction: Prefabricated homes and housing components, such as walls, floors, and roof trusses, are used to expedite the construction of single-family homes, multi-family buildings, and residential communities.
2. Multi-family Housing: Prefabricated modules or units are utilized in the construction of apartment buildings, condominiums, and townhouses to streamline the building process and reduce construction time.
3. Affordable Housing: Prefabricated construction methods are employed to create affordable housing solutions, including modular housing projects and temporary housing for low-income communities.
4. Mixed-Use Developments: Prefabricated components are integrated into mixed-use developments, combining residential, commercial, and retail spaces to create vibrant urban environments with efficient construction processes.
5. Commercial Buildings: Prefabrication is used in the construction of office buildings, retail centers, and mixed-use commercial developments to accelerate project timelines, reduce costs, and achieve design flexibility.
6. Hospitality Projects: Prefabricated hotel rooms, resort villas, and lodging units are utilized in the hospitality sector to deliver high-quality accommodations with faster construction schedules and minimized disruptions.
7. Student Housing: Prefabricated modules or dormitory units are employed in the construction of student housing complexes, providing cost-effective and scalable solutions for university campuses.
8. Senior Living Communities: Prefabricated construction methods are utilized in the development of senior living facilities, including assisted living and retirement communities, to create comfortable and accessible housing options for older adults.
9. Sustainable Development: Prefabrication allows for the integration of sustainable building practices, such as energy-efficient design, green materials, and renewable energy systems, to create environmentally friendly real estate developments
Market potential of prefabrication construction
In India, the prefabricated construction methodologies remain largely untapped today. The prefabricated industry in India is largely bifurcated by materials like concrete, glass, metal, timber etc. It is primarily used in residential, commercial, industrial and infrastructure projects. There are few government schemes like “Housing for All” under Pradhan Mantri Awash Yojana (PMAY) which adopt precast technology for constructing residential dwelling units. Many commercial buildings are adopting pre-cast systems for fast tracking construction and many infrastructure projects are using precast systems in flyover and road construction for fast paced infrastructural developments. However, there is a long way to go for a full-fledged adoption of prefabricated construction.
As per mordorintelligence report, The size of India prefabricated buildings market is USD 2.3 billion in the current year and is anticipated to register a CAGR of over 13% during 2024 to 2029.
As per Colliers reports from web-based sources, the prefabricated building market in India is USD 2.3 billion in current financial year and is expected to grow with a CAGR of approximately 13% in the next five years.
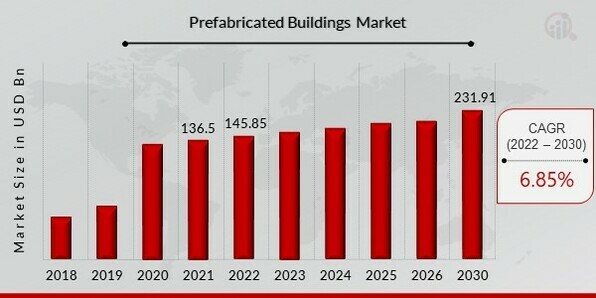
As per Market Research Future report, Prefabricated Buildings Market Size was valued at USD 136.5 billion in 2021. The Prefabricated Buildings market industry is projected to grow from USD 145.85 Billion in 2022 to USD 231.91 billion by 2030, exhibiting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.85% during the forecast period (2024 - 2030).The region's expanding demand for traditional procedures and its burgeoning urban population are the key market drivers enhancing the market growth for prefabricated buildings.
There is a big opportunity for prefab companies in India, and hundreds of thousands of plants are expected to be required in the future. Over the next few years, India will feature among the fastest-growing countries in terms of construction output, making technology intervention a key component. India is expected to become the third-largest construction market in the world by 2025.
The demand for prefabrication in India has been steadily increasing due to several factors:
1. Rapid Urbanization: India is experiencing rapid urbanization, leading to a growing demand for affordable housing, infrastructure, and commercial developments in urban areas. Prefabrication offers a faster and more efficient construction solution to meet this demand.
2. Housing Shortage: There is a significant shortage of housing in India, particularly in urban areas, resulting in a need for faster and more scalable construction methods. Prefabricated housing solutions can help address this shortage by accelerating the construction process and providing affordable housing options.
3. Infrastructure Development: India's ambitious infrastructure development plans, including highways, bridges, railways, airports, and metro systems, require efficient construction methods to meet deadlines and budget constraints. Prefabrication can help expedite the construction of infrastructure projects while minimizing disruptions and costs.
4. Government Initiatives: The Indian government has been promoting prefabrication as part of its efforts to promote affordable housing, sustainable development, and Make in India initiatives. Various policies, incentives, and subsidies are encouraging the adoption of prefabricated construction methods by developers and contractors.
5. Technology Adoption: Advances in construction technology and manufacturing processes have made prefabrication more viable and cost-effective in India. Improved design software, automation, robotics, and digital fabrication techniques are driving innovation in the prefabrication industry.
6. Quality and Sustainability: Prefabrication offers advantages in terms of quality control, waste reduction, energy efficiency, and environmental sustainability. As awareness of these benefits grows, developers, investors, and end-users are increasingly turning to prefabricated construction solutions.
Conclusion
Prefabrication stands as a game-changer in the construction industry, offering a streamlined and efficient approach to building construction. By manufacturing building components off-site in controlled environments, prefabrication not only accelerates construction timelines but also enhances quality, reduces costs, and promotes sustainability. From modular construction and panelized systems to prefabricated components and volumetric units, a variety of prefabrication methods cater to diverse project needs and requirements. With factors such as rapid urbanization, housing shortages, infrastructure development, and advancements in construction technology driving its demand, prefabrication is poised to play a crucial role in shaping the future of building construction, offering practical solutions, innovation, and sustainable development opportunities in the built environment.








.png)