Adhesives in construction are specialised construction materials designed to securely bond various materials together without the need for mechanical fasteners. They play a crucial role in modern construction projects by providing strong and durable connections between different surfaces. Adhesives are used to join materials such as wood, metal, concrete, glass, and plastics, offering versatility in creating structures and assemblies.
Adhesives also provide enhanced aesthetics by eliminating visible fasteners and seam lines, resulting in cleaner and more seamless finishes. Additionally, they can improve the structural integrity of joints and connections by evenly distributing loads and minimizing the risk of corrosion or weakening associated with mechanical fasteners. Overall, adhesives contribute to the efficiency, durability, and aesthetic appeal of construction projects, making them indispensable in modern building practices.
Advantages of Adhesives in Construction
1. Uniform Stress Distribution: Adhesives excel in distributing stress uniformly across bonded surfaces, a key advantage over traditional mechanical fasteners. When subjected to loads or forces, adhesives create a bond that spreads stresses evenly, minimizing the risk of stress concentrations and potential failure points. This characteristic enhances the structural integrity of constructions, particularly in applications where dynamic loads or environmental stresses are prevalent. By mitigating stress concentrations, adhesives contribute to the longevity and durability of structures.
2. Versatility in Bonding Materials: One of the most significant advantages of adhesives is their versatility in bonding various materials. From wood and metal to concrete and plastics, adhesives can securely join dissimilar materials, enabling the creation of innovative designs and assemblies. This versatility expands the possibilities for architects and engineers, allowing them to explore new construction techniques and materials combinations. Additionally, adhesives facilitate the assembly of lightweight structures with complex geometries, enhancing design flexibility and efficiency.
3. Aesthetic Enhancement: Adhesives offer aesthetic benefits by eliminating visible fasteners and seam lines, resulting in cleaner and more seamless finishes. Unlike mechanical fasteners, which may disrupt the visual appearance of surfaces, adhesives create a smooth and uninterrupted surface, enhancing the overall aesthetics of structures and assemblies. This aesthetic enhancement is particularly valuable in architectural applications where visual appeal is paramount, such as in interior finishes and exterior cladding systems.
4. Weight Reduction: Adhesives contribute to weight reduction in constructions, offering a lightweight alternative to traditional mechanical fasteners. By eliminating the need for bulky fasteners like screws and bolts, adhesives create lightweight assemblies, which is especially advantageous in applications where weight is a concern, such as aerospace and automotive industries. The reduction in weight can lead to cost savings in materials and transportation, as well as improved energy efficiency in structures.
5. Corrosion Resistance: Unlike metal fasteners, which may be susceptible to corrosion, adhesives offer corrosion resistance, making them suitable for applications exposed to moisture or harsh environments. Adhesives create a barrier between bonded surfaces, preventing the ingress of moisture and contaminants that can lead to corrosion. This corrosion resistance extends the lifespan of constructions, reducing maintenance requirements and enhancing long-term durability.
6. Vibration Dampening: Adhesives have the ability to dampen vibrations and reduce noise, improving the performance of structures and assemblies. By absorbing and dissipating vibrational energy, adhesives help to minimize noise transmission and vibration-induced fatigue, enhancing occupant comfort and safety. This vibration dampening property is particularly beneficial in applications such as automotive components, machinery, and building structures subjected to dynamic loads.
7. Ease of Application: Adhesives offer ease and flexibility in application, with a variety of methods available for their use. They can be applied quickly and easily using techniques such as spraying, rolling, or dispensing, making them convenient for large-scale or complex projects. This ease of application contributes to increased efficiency and productivity in construction processes, reducing labor costs and construction timelines.
8. Environmental Benefits: Many adhesives are formulated to be environmentally friendly, with low VOC emissions and minimal impact on indoor air quality. These environmentally friendly adhesives align with sustainable construction practices, contributing to healthier indoor environments and reducing the overall environmental footprint of construction projects. By choosing eco-friendly adhesives, builders and designers can support sustainability goals while still achieving high-performance bonding solutions
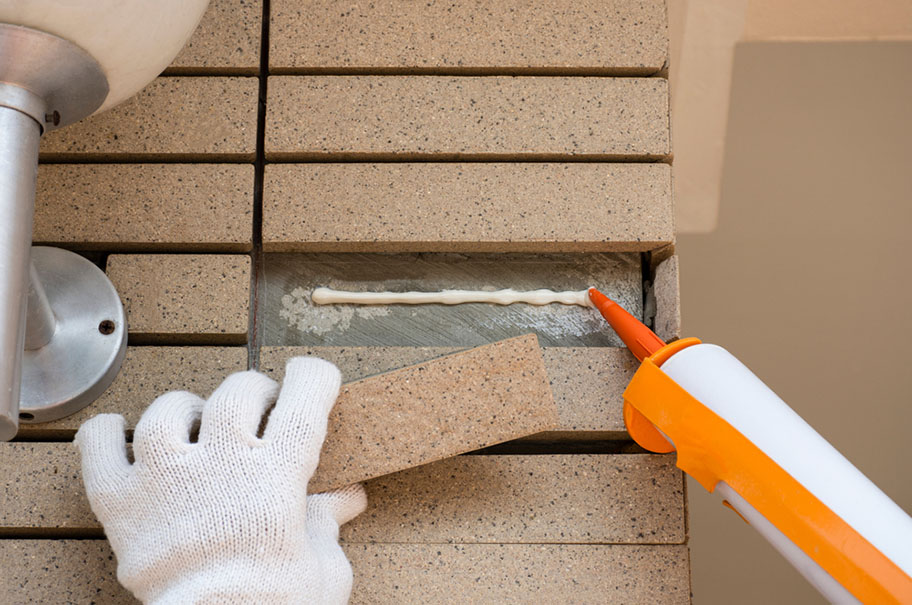

Types of Adhesives used in Construction
1. Polyurethane Adhesives: Polyurethane adhesives are versatile bonding agents widely used in construction for their high strength and durability. They provide excellent adhesion to various materials, including wood, metal, plastics, and concrete, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. Polyurethane adhesives offer superior resistance to moisture, chemicals, and temperature fluctuations, making them ideal for both indoor and outdoor use. Their ability to withstand harsh environmental conditions makes them particularly well-suited for structural bonding applications where long-term durability is essential. Additionally, polyurethane adhesives cure to a flexible and resilient finish, allowing for some degree of movement or expansion in bonded joints, which is beneficial in construction applications subjected to dynamic loads or vibrations.
2. Epoxy Adhesives: Epoxy adhesives are renowned for their exceptional bonding strength and durability, making them a popular choice in construction for bonding materials such as concrete, metal, and composites. Epoxy adhesives consist of two components – a resin and a hardener – that must be mixed together before application. Once mixed, epoxy adhesives cure to a hard and rigid finish, offering high-strength bonds that withstand heavy loads and harsh environmental conditions. They provide excellent resistance to moisture, chemicals, and heat, making them suitable for demanding structural applications where long-term performance is critical. Epoxy adhesives are commonly used in construction for bonding structural elements, repairing concrete surfaces, and assembling composite materials.
3. Acrylic Adhesives: Acrylic adhesives are fast-curing bonding agents known for their strong adhesion to a variety of materials, including plastics, metals, and glass. They offer good weather resistance and are commonly used in construction for exterior applications such as bonding facade elements, cladding, and curtain walls. Acrylic adhesives cure to a clear and flexible finish, providing durable bonds that withstand temperature fluctuations and environmental exposure. They offer excellent UV resistance, making them suitable for outdoor use without yellowing or deteriorating over time. Additionally, acrylic adhesives provide flexibility and impact resistance, making them ideal for applications requiring dynamic loads or vibrations, such as automotive components and building structures.
4. Construction Sealants: Construction sealants play a vital role in sealing joints, gaps, and penetrations in construction materials to prevent water infiltration, air leakage, and moisture damage. Silicone sealants and polyurethane sealants are commonly used in construction for their excellent adhesion and durability. Silicone sealants offer superior flexibility and weather resistance, making them ideal for exterior applications where movement and exposure to harsh weather conditions are prevalent. Polyurethane sealants provide strong adhesion to a variety of substrates and offer excellent resistance to moisture, chemicals, and temperature fluctuations, making them suitable for both interior and exterior sealing applications. Construction sealants are applied in joints and gaps in building envelopes, windows, doors, and other construction elements to ensure watertight and airtight seals that contribute to the overall integrity and performance of the structure.
5. Contact Adhesives: Contact adhesives are versatile bonding agents that offer instant adhesion upon contact with both surfaces to be bonded. They are commonly used in construction for bonding large surface areas or materials with irregular shapes. Contact adhesives consist of solvent-based or water-based formulations and are applied to both surfaces, allowed to dry, and then pressed together to form a strong bond. They provide excellent adhesion to a wide range of materials, including laminates, veneers, and decorative surfaces. Contact adhesives offer high initial strength and bond integrity, making them suitable for applications where immediate bonding and holding power are essential, such as laminate bonding, veneer application, and bonding decorative surfaces in furniture and cabinetry.
6. Structural Adhesives: Structural adhesives are specialized bonding agents designed to provide load-bearing strength and structural integrity to bonded joints in construction applications. They offer high strength and durability, making them suitable for bonding structural panels, composite materials, and load-bearing components. Structural adhesives are often used in applications where mechanical fasteners are impractical or undesirable, such as bonding structural elements in aerospace, automotive, and marine industries. They provide uniform stress distribution and excellent resistance to moisture, chemicals, and temperature fluctuations, ensuring long-term performance and reliability in demanding structural applications.
7. Vinyl Adhesives: Vinyl adhesives are specifically formulated for bonding vinyl flooring materials, including vinyl tiles, planks, and sheet vinyl, to subfloors. They provide strong and durable bonds on various substrates, including concrete, wood, and plywood. Vinyl adhesives offer excellent resistance to moisture and temperature fluctuations, making them ideal for use in high-moisture environments such as kitchens, bathrooms, and commercial spaces. They come in both solvent-based and water-based formulations and offer fast curing times, allowing for quick and efficient flooring installations. Vinyl adhesives provide a secure and stable bond that withstands heavy foot traffic and daily wear and tear, ensuring long-lasting and durable flooring installations.
8. Polyurethane Foam Adhesives: Polyurethane foam adhesives are specifically designed for bonding insulation materials such as rigid foam boards, polystyrene, and polyurethane foam panels in construction applications. They provide strong adhesion to a variety of substrates and offer excellent thermal insulation properties, making them ideal for insulation applications in buildings and structures. Polyurethane foam adhesives expand upon curing to fill gaps and voids, providing a tight seal and enhancing the thermal performance of the insulation system. They are commonly used in both residential and commercial construction for insulating walls, roofs, and foundations, helping to improve energy efficiency and reduce heating and cooling costs.
9. Cyanoacrylate Adhesives (Super Glue): Cyanoacrylate adhesives, commonly known as super glue, are fast-acting and versatile adhesives used in construction for bonding a wide range of materials, including plastics, metals, rubber, and ceramics. They offer rapid curing times and high bond strength, making them suitable for quick repairs and assembly tasks. Cyanoacrylate adhesives form strong bonds within seconds upon contact with surfaces, providing instant adhesion. They are often used in construction for bonding small components, repairing household items, and securing fasteners in hard-to-reach areas.
10. Hot Melt Adhesives: Hot melt adhesives, also known as hot glue, are thermoplastic adhesives that are melted and applied in a liquid state before solidifying upon cooling. They are commonly used in construction for temporary bonding, packaging, and assembly applications. Hot melt adhesives offer fast setting times and good bond strength on a variety of substrates, making them suitable for bonding materials like paper, cardboard, plastics, and wood. They are applied using hot glue guns, which melt the adhesive and dispense it onto the desired surfaces. Once cooled, hot melt adhesives form strong and durable bonds, providing temporary or permanent adhesion as required.
11. Pressure-Sensitive Adhesives (PSAs): Pressure-sensitive adhesives (PSAs) are tacky adhesives that adhere to surfaces upon application of slight pressure. They offer immediate adhesion and can be removed without leaving residue behind, making them ideal for temporary bonding applications. PSAs are commonly used in construction for mounting signage, posters, and temporary protective coverings. They are also used in the manufacture of adhesive tapes and labels for packaging, marking, and identification purposes. PSAs come in various formulations, including acrylic, rubber, and silicone-based adhesives, offering different levels of tackiness and adhesion strength to suit specific application requirements.
12. Wood Adhesives: Wood adhesives, also known as woodworking adhesives, are specialized adhesives used for bonding wood materials in construction and carpentry applications. They offer strong and durable bonds that withstand the rigors of woodworking and structural assembly. Wood adhesives come in various formulations, including polyvinyl acetate (PVA), urea formaldehyde (UF), and epoxy-based adhesives, each tailored for specific wood bonding applications. They provide excellent adhesion to wood substrates and offer resistance to moisture, heat, and environmental factors. Wood adhesives are commonly used in construction for bonding wood panels, furniture assembly, cabinetry, and woodworking projects.

Applications of Adhesives in Construction
1. Flooring Installation:
Adhesives play a critical role in the installation of various types of flooring materials in construction projects. For instance, in the installation of vinyl tiles or sheet flooring, vinyl adhesive is applied to the subfloor to create a strong bond between the flooring material and the substrate. Similarly, in the installation of hardwood flooring or laminate flooring, flooring adhesive is used to adhere the individual planks or tiles to the subfloor. Flooring adhesives provide several benefits, including strong adhesion, stability, and durability. They ensure that the flooring material remains securely in place, even in high-traffic areas, and they contribute to the overall longevity of the floor system. Additionally, flooring adhesives offer moisture resistance, which is essential for maintaining the integrity of the flooring material over time.
2. Wall Cladding and Paneling:
Adhesives are widely used for bonding wall cladding materials such as stone veneer, ceramic tiles, and composite panels to building surfaces. These adhesives provide a secure bond between the cladding material and the substrate, ensuring stability and durability. For example, in the installation of ceramic tiles, tile adhesive is applied to the substrate using a trowel, and the tiles are then pressed into the adhesive. The adhesive cures to create a strong and permanent bond between the tiles and the wall surface. Similarly, in the installation of stone veneer or composite panels, construction adhesive is used to bond the cladding material to the substrate. Adhesive bonding eliminates the need for mechanical fasteners, resulting in a clean and seamless appearance.
3. Facade Systems:
Adhesives play a vital role in the installation of facade systems, including curtain walls, rainscreens, and insulated panels. Structural adhesives are used to bond facade components such as glass, aluminum, and composite panels to the building structure. These adhesives provide load-bearing strength and stability to the facade system, allowing it to withstand wind loads, thermal expansion, and other environmental stresses. Additionally, adhesive bonding eliminates the need for visible fasteners, creating a sleek and modern aesthetic. Facade adhesives offer excellent weather resistance, preventing water infiltration and moisture damage, and contributing to the overall durability and performance of the building envelope.
4. Insulation Installation:
Adhesives are commonly used for bonding insulation materials such as rigid foam boards, polystyrene, and fiberglass batts to building substrates. Insulation adhesives provide strong and durable bonds, ensuring that the insulation material remains securely in place. For example, in the installation of rigid foam insulation, construction adhesive is applied to the back of the insulation panels, and the panels are then pressed onto the wall or roof surface. The adhesive cures to create a rigid bond between the insulation and the substrate, preventing air leakage and thermal bridging. Insulation adhesives offer excellent thermal insulation properties, enhancing the energy efficiency of the building and reducing heating and cooling costs. Additionally, they provide acoustic insulation, reducing sound transmission and improving indoor comfort.
5. Roofing Systems:
Adhesives are essential in the installation of roofing materials, contributing to the integrity and longevity of the roof system. In roofing applications, adhesives are used to bond various roofing materials such as membranes, shingles, and tiles to the roof substrate. For instance, in the installation of single-ply roofing membranes, adhesive is applied to the underside of the membrane and adhered directly to the roof deck. This creates a watertight seal that protects the building from water infiltration and weather damage. Adhesives also play a crucial role in the installation of roofing shingles or tiles, providing secure attachment and preventing wind uplift. Additionally, roofing adhesives offer flexibility and durability, allowing the roof system to accommodate thermal expansion and contraction without compromising performance.
6. Window and Door Installation:
Adhesives are utilized in the installation of windows, doors, and trim components, providing secure attachment and weatherproofing. Window and door adhesives are applied to the perimeter of the window or door frame before installation, creating a watertight seal and preventing air leakage. This helps to improve the energy efficiency of the building and enhance indoor comfort. Adhesives also provide structural support, ensuring that windows and doors remain securely in place, even in high winds or adverse weather conditions. Additionally, adhesive bonding eliminates the need for mechanical fasteners, resulting in a cleaner and more streamlined appearance.
7. Interior Finishes:
Adhesives are commonly used in the installation of interior finishes such as wall coverings, ceiling tiles, and decorative moldings. For example, in the installation of wallpaper or wall coverings, wallpaper adhesive is applied to the back of the wallpaper and adhered directly to the wall surface. This creates a smooth and seamless finish, enhancing the aesthetic appeal of the interior space. Adhesives are also used to bond ceiling tiles to the ceiling substrate, providing acoustic insulation and enhancing the appearance of the room. Additionally, adhesives are used to attach decorative moldings such as baseboards, crown molding, and chair rails, adding architectural detail and visual interest to the space.
8. Structural Bonding:
Adhesives play a vital role in structural bonding applications, providing load-bearing strength and stability to bonded joints. Structural adhesives are used to bond structural components such as beams, columns, and panels in building construction. These adhesives create strong and durable bonds that distribute loads evenly across the bonded surfaces, ensuring structural integrity and stability. Structural adhesives offer several advantages over traditional mechanical fasteners, including reduced weight, improved aesthetics, and increased design flexibility. They are commonly used in applications where welding or mechanical fastening is impractical or undesirable, such as bonding composite materials or joining dissimilar substrates.
9. Sealing and Caulking:
Adhesives are extensively used for sealing joints, gaps, and penetrations in building materials to prevent air leakage, water infiltration, and moisture damage. Sealant adhesives are applied along joints between building components such as windows, doors, and trim, as well as gaps around pipes, ducts, and electrical conduits. They provide a flexible and durable seal that accommodates movement and thermal expansion, ensuring long-term performance and weather resistance. Sealant adhesives come in various formulations, including silicone, polyurethane, and acrylic, each offering specific properties such as adhesion, flexibility, and weatherability. They play a crucial role in maintaining the integrity of the building envelope and enhancing energy efficiency by reducing air leakage and heat loss.
10. Repair and Maintenance:
Adhesives are commonly used for repairing and bonding building components such as concrete, masonry, wood, and metal. Repair adhesives provide strong and durable bonds, allowing for the restoration of damaged or deteriorated structures. For example, epoxy adhesives are used for concrete repair, bonding new concrete to existing surfaces to fill cracks, patch holes, and reinforce structural elements. Wood adhesives are used for repairing furniture, cabinets, and trim, providing a strong bond that restores structural integrity and aesthetics. Metal adhesives are used for bonding metal components in automotive, marine, and industrial applications, offering high strength and corrosion resistance. Adhesives play a vital role in maintenance activities, extending the lifespan of buildings and infrastructure by repairing damage and preventing further deterioration.
Construction Adhesive’s Market Potential in India
The construction adhesives market in India is expected to grow at a robust rate over the next five years. According to Construction Times, the Indian adhesive and sealant market was valued at around Rs 10,100 crore in 2020 and is expected to reach around Rs 15,000 crore in 2025.
As per BlueWeave Consulting report, The India Adhesives and Sealants Market size was estimated at USD 2.155 billion in 2023. During the forecast period between 2024 and 2030, the India Adhesives and Sealants Market size is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.12% reaching a value of USD 3.057 billion by 2030.
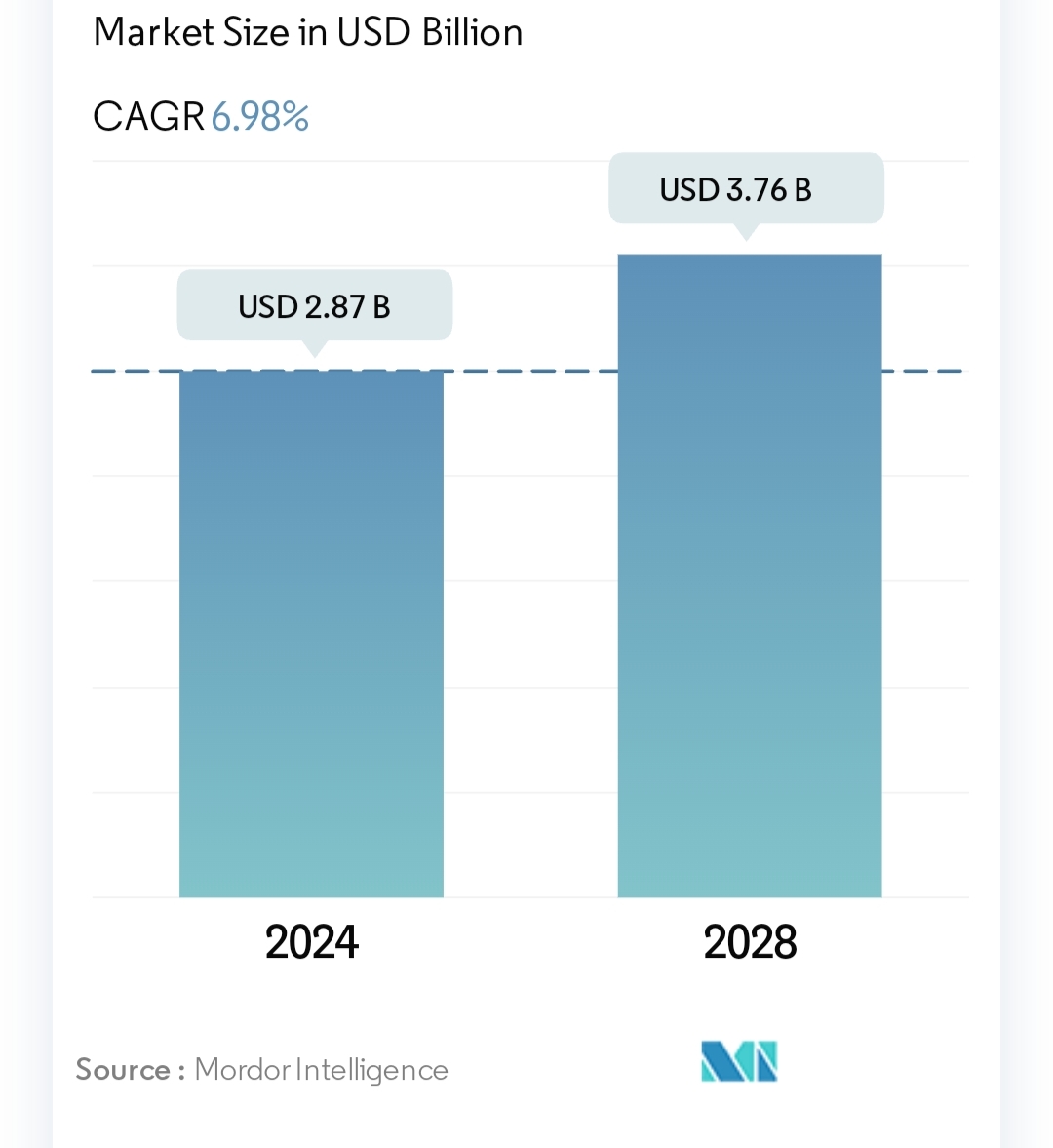
As per Mordor Intelligence report, The India Adhesives Market is expected to reach USD 2.87 billion in 2024 and grow at a CAGR of 6.98% to reach USD 3.76 billion by 2028.
Conclusion
The use of adhesives in construction has become increasingly prevalent due to their versatility, strength, and efficiency. This article has highlighted the various reasons behind the growing demand for adhesives in the construction industry. From their ability to bond a wide range of materials together to their contribution to design flexibility and sustainability, adhesives play a crucial role in modern construction practices. Advancements in adhesive technology continue to drive innovation, offering solutions that meet the evolving needs of builders, contractors, and architects.
As construction projects become more complex and demanding, adhesives provide reliable solutions for structural bonding, insulation installation, waterproofing, and repair applications. Moreover, their environmental benefits, cost-effectiveness, and ease of application further contribute to their widespread adoption.
Looking ahead, the continued growth of the construction industry, coupled with ongoing advancements in adhesive technology, is expected to sustain the market demand for adhesives in construction. By embracing these innovative solutions, stakeholders in the construction sector can enhance efficiency, performance, and sustainability across a diverse range of projects.
Cover image- senepolsantaluzia.com








.png)