LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) is a cutting-edge technology that is transforming the construction and infrastructure sectors by enabling precise 3D mapping. By using laser pulses to measure distances and generate detailed spatial data, LiDAR is streamlining project planning, monitoring, and asset management. From land surveying and progress tracking to infrastructure inspection and maintenance, this technology is driving efficiency and accuracy across various applications.
Key Components of a LiDAR System:
- Laser Emitter: Generates rapid pulses of laser light.
- Sensor/Receiver: Captures the reflected laser pulses.
- GPS and IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit): Determines the sensor’s precise location and orientation.
- Data Processor: Converts raw signals into a structured 3D representation known as a point cloud.
LiDAR Data Processing and Interpretation
Once the LiDAR system collects point cloud data, it undergoes several processing steps:
- Filtering: Removing noise and irrelevant data.
- Classification: Categorizing data into surfaces, buildings, vegetation, and more.
- Digital Elevation Model (DEM) Generation: Creating usable terrain maps.
- Integration with GIS and BIM: Enabling informed decision-making in urban planning and infrastructure projects.
Types of LiDAR Systems
LiDAR systems can be classified based on their mode of operation and application.
Airborne LiDAR
Airborne LiDAR is mounted on aerial platforms such as drones, airplanes, or helicopters. It is primarily used for large-scale mapping and terrain analysis. It enables the rapid collection of high-resolution topographic data, making it useful for applications such as flood modeling, forest management, and urban planning. Airborne LiDAR can be further categorized into topographic LiDAR, which maps land surface features, and bathymetric LiDAR, which uses water-penetrating laser beams to map underwater environments.
Terrestrial LiDAR
Terrestrial LiDAR operates from ground-based platforms, including stationary tripods and mobile scanning vehicles. This type of LiDAR is commonly used for urban development, infrastructure planning, and structural analysis. It provides highly detailed 3D models of buildings, roads, and bridges, assisting in construction monitoring and historical site documentation. Terrestrial LiDAR is widely employed in construction projects to enhance accuracy in measurements and detect structural deformations.
Mobile LiDAR
Mobile LiDAR is mounted on moving vehicles such as cars, trains, or boats. This system is extensively used for road mapping, railway tracking, and asset management. Mobile LiDAR efficiently captures high-density data while in motion, allowing for continuous updates of infrastructure networks. It is particularly beneficial for smart city applications, where real-time traffic monitoring and navigation systems require precise spatial information.
Handheld LiDAR
Handheld LiDAR consists of compact, portable devices that are increasingly being integrated into various applications, including industrial inspections, forensic investigations, and augmented reality (AR). These scanners are used for close-range mapping and object detection, making them valuable in industries like manufacturing and crime scene reconstruction. Recent advancements in consumer electronics have also led to the incorporation of LiDAR sensors in smartphones, enhancing AR applications and indoor spatial mapping.
The Role of LiDAR in Construction and Infrastructure
Land Surveying and Site Planning
LiDAR provides a faster and more accurate alternative to traditional surveying methods, improving terrain mapping, elevation modeling, and site analysis for better project planning.
Construction Progress Monitoring
Periodic LiDAR scans help track project progress in real time, compare actual conditions with planned designs, and detect deviations early, minimizing costly rework.
Structural Quality Control
LiDAR ensures precise detection of misalignments, cracks, and inconsistencies, enhancing compliance with safety and quality standards and improving overall structural integrity.
Infrastructure Asset Management
Detailed digital models of bridges, roads, and buildings created using LiDAR support predictive maintenance, helping prevent failures and extend asset lifespan.
Road and Highway Construction
LiDAR assists in terrain analysis, obstacle identification, and grading verification, ensuring roads are built to design specifications and safety standards.
Bridge Inspection and Maintenance
High-resolution 3D LiDAR scans detect surface cracks and structural deformities, reducing reliance on manual inspections and enhancing safety.
Railway and Metro Development
LiDAR enables precise track alignment, tunnel clearance analysis, and obstacle detection, ensuring efficient and safe railway expansion.
Pipeline and Utility Infrastructure
LiDAR is used for underground pipeline mapping, leak detection, and structural integrity monitoring, reducing environmental risks and ensuring reliability.
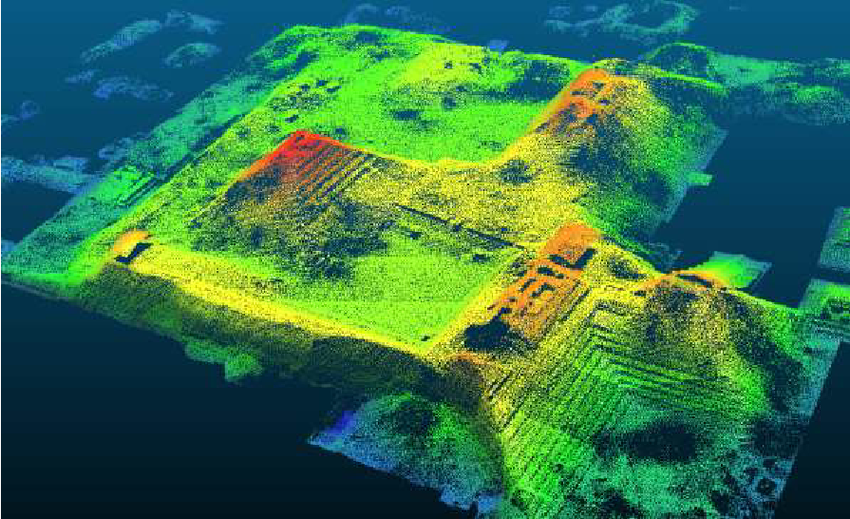

LiDAR Technology in India
India has recognized LiDAR as a valuable tool for geospatial applications and infrastructure development. Organizations such as the Survey of India (SOI), National Remote Sensing Centre (NRSC), and Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) have incorporated LiDAR into various projects.
- Smart Cities Initiative: Supporting urban planning and intelligent traffic management.
- Forestry and Environmental Conservation: Mapping deforestation and assessing carbon stocks.
- Disaster Management: Assisting in flood modeling, landslide prediction, and damage assessment.
- Transportation Infrastructure: Enhancing railway and highway planning and maintenance.
- Water Resource Management: Supporting watershed mapping and irrigation planning.
The increasing adoption of LiDAR in India reflects the country’s commitment to leveraging advanced technology for sustainable and efficient infrastructure development.
Expanding LiDAR Applications and Market Growth in India
The India LiDAR market is experiencing significant growth, driven by its expanding applications in disaster management, infrastructure development, and geospatial analysis. LiDAR’s capability to generate real-time, high-precision data makes it indispensable for flood monitoring, earthquake response, and rescue operations. The modernization of railway infrastructure is a key factor propelling demand, as LiDAR enables accurate railway alignment, track design, and maintenance planning.
Government initiatives promoting renewable energy, environmental conservation, and workplace safety are further accelerating LiDAR adoption. The technology is crucial for optimizing wind energy planning and solar farm layouts, aligning with India’s renewable energy expansion goals. Additionally, LiDAR supports environmental efforts through applications in forest management, soil erosion analysis, and wildlife habitat studies. The enforcement of stringent occupational safety regulations in the mining and construction sectors is also driving demand for LiDAR-based monitoring and risk assessment. With a growing base of skilled professionals in geospatial technologies and remote sensing, LiDAR is becoming an essential tool for precise, data-driven planning and development across multiple industries in India.
India LiDAR Market Potential
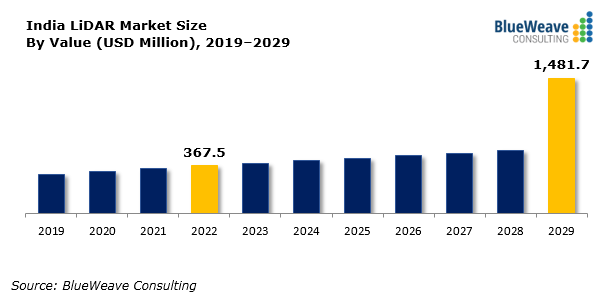
As per Blue Weave Consulting Report, the India LiDAR market was valued at USD 367.5 million in 2022 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 22.04% during 2023–2029, reaching USD 1,481.7 million by 2029. The increasing adoption of LiDAR-based digital terrain models for applications such as inland waterways monitoring, hillside change detection, and water runoff analysis in mining and agriculture is driving market expansion. Automation in LiDAR systems is also expected to reduce labor costs and enhance productivity, further propelling growth. The India LiDAR market features a mix of domestic and international players, with companies focusing on technological advancements and strategic partnerships to strengthen their market presence.
Top LiDAR companies in India:
- Genesys – pProvides mapping and surveying solutions, offering geospatial services across multiple sectors.
- Rolta – Provides IT and geospatial solutions, specializing in image processing, mapping, and spatial data analysis.
- Ceinsys – Offers geospatial and IT solutions with expertise in mobile, airborne, and terrestrial LiDAR.
- Nakshatech – Focuses on LiDAR data collection, topographical classifications, feature extraction, and contour generation.
- Geokno – Specializes in LiDAR applications, providing airborne, mobile, and terrestrial LiDAR sensors.
- Aerial Geomatics – Provides services in image processing, point cloud generation, and geospatial analysis.
- Altitud Digitals India – Offers planning, analytics, impact studies, and risk management using LiDAR technology.
- Atlaspoint Tech – Specializes in mapping accuracy, geospatial data processing, and high-quality mapping products.
- Deduce Technologies – Focuses on AI-driven geo-analytics and geospatial data services.
- Intraspatial – Provides photogrammetry mapping, orthophoto generation, satellite imagery, and LiDAR data editing.
Indian Government Initiatives Driving LiDAR Adoption in India
One of the key initiatives promoting LiDAR adoption in India is the LiDAR-based forest area survey, covering ten states—Assam, Bihar, Chhattisgarh, Goa, Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Manipur, Nagaland, and Tripura. The project was awarded to WAPCOS, a Mini Ratna PSU under the Jal Shakti Ministry, and launched in July 2020 with a budget exceeding ₹18 crore. This initiative supports forest management, disaster preparedness, and environmental monitoring, enabling authorities to make data-driven decisions for conservation and sustainable land use.
Another significant driver is infrastructure development initiatives, particularly the National Infrastructure Pipeline (NIP), which has outlined projects worth INR 111 trillion by 2025. As LiDAR plays a crucial role in surveying, mapping, and monitoring large-scale infrastructure projects, its adoption is increasing across sectors such as transportation, urban planning, and construction. By providing high-precision geospatial data, LiDAR enhances project planning efficiency and execution accuracy, reducing errors and optimizing resources.
Additionally, government support for geospatial technologies has accelerated the growth of LiDAR applications in India. The 2021 Geospatial Data Policy encourages private sector participation, leading to the involvement of over 300 companies in LiDAR-based mapping, data collection, and geospatial analytics. This policy has expanded the use of LiDAR in urban planning, smart city projects, and industrial development, fostering innovation and boosting efficiency across multiple industries.
The integration of AI and machine learning with LiDAR is expected to enhance automation in data processing and predictive maintenance. Additionally, Building Information Modeling (BIM) and Digital Twin technology will allow for real-time infrastructure monitoring and proactive decision-making.
In India, government initiatives such as smart cities, highway expansions, and flood resilience programs will further drive LiDAR adoption. As costs decline and computational capabilities improve, LiDAR will become more accessible to mid-sized construction firms, expanding its impact across the industry.
Conclusion
LiDAR is transforming the construction and infrastructure sectors by providing unmatched precision and efficiency in mapping and monitoring. With its growing adoption in India and globally, LiDAR is set to play a key role in the development of smart cities, resilient infrastructure, and sustainable urban planning. As advancements continue, integrating LiDAR with AI-driven analytics will further enhance project execution, making construction smarter, safer, and more cost-effective.










.png)