An HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) system is a comprehensive technology that regulates indoor climate and air quality in various settings, including residential, commercial, and industrial environments. It combines heating to provide warmth, ventilation to circulate and filter air, and air conditioning to cool and dehumidify spaces. Advanced control systems manage temperature, humidity, and airflow to ensure a comfortable and healthy indoor environment. Modern HVAC systems utilize energy-efficient technologies, smart controls, and innovative designs to optimize performance and reduce energy consumption, playing a crucial role in maintaining indoor comfort and environmental sustainability.
Basic Components of an HVAC System
HVAC systems are complex systems designed to control temperature, humidity, air quality, and air movement within a building or a confined space. Here are the basic components:
- Thermostat: The control center for the HVAC system, allowing users to set the desired temperature and control the system’s operation.
- Furnace/Heat Pump: In heating systems, a furnace burns fuel (such as gas or oil) to produce heat, while a heat pump extracts heat from the outside air or ground and transfers it indoors.
- Air Conditioner: Cools indoor air by removing heat and moisture from it, using a refrigerant to facilitate the heat exchange process.
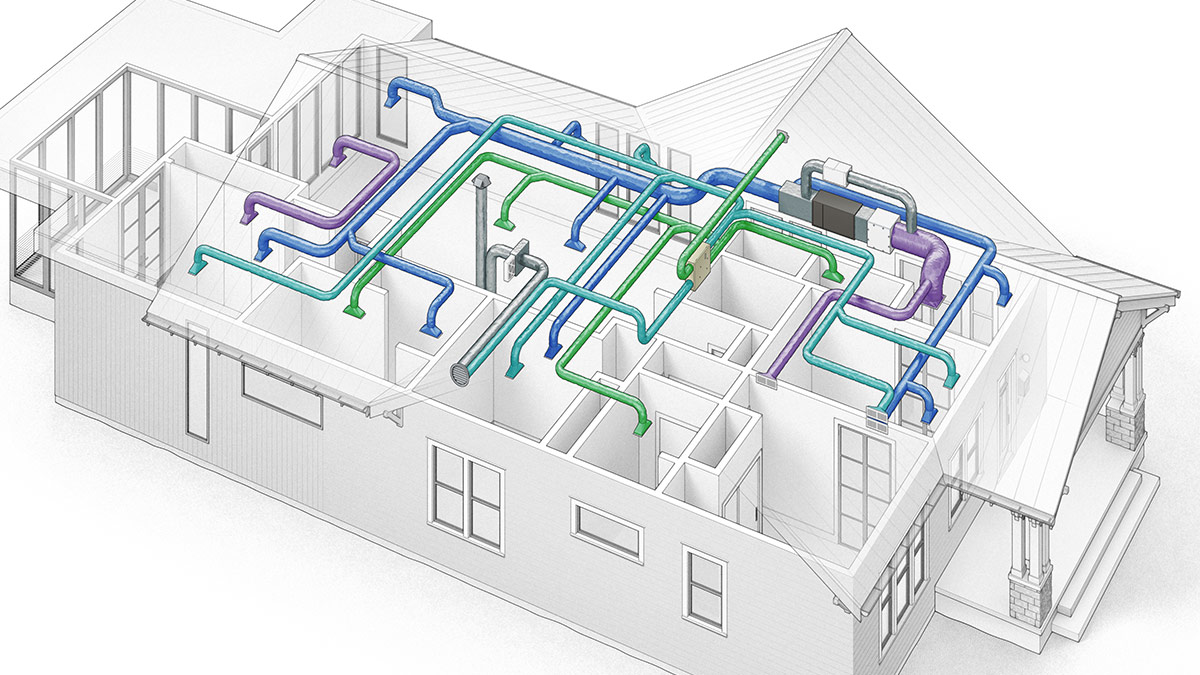
- Ductwork: Pathways that distribute heated or cooled air from the HVAC system to different rooms or zones within a building and return air back to the system for reconditioning.
- Air Filters: Placed in the return air ducts to trap dust, dirt, allergens, and other particulates, improving indoor air quality and protecting the HVAC system’s components from damage.
- Blower Fan: Responsible for circulating air throughout the ductwork and into the living spaces of a building.
- Vents/Registers: Openings in walls, floors, or ceilings where air is delivered into the rooms.
- Humidifier/Dehumidifier: Some HVAC systems include humidifiers to add moisture to dry indoor air during the heating season, while dehumidifiers remove excess moisture from humid air during the cooling season.
- Thermal Expansion Valve/Orifice: Regulates the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator coil, controlling the rate at which the refrigerant evaporates and absorbs heat from indoor air.
Advantages of HVAC System
- Enhanced Comfort: Regulates temperature and humidity, ensuring a comfortable indoor environment year-round.
- Improved Air Quality: Filters and circulates air, reducing allergens, dust, and pollutants for healthier living conditions.
- Energy Efficiency: Modern systems are designed to be energy-efficient, reducing energy consumption and lowering utility bills.
- Temperature Control: Provides precise control over indoor temperatures, accommodating varying needs across different zones or rooms.
- Consistent Climate: Maintains a steady indoor climate, preventing extreme fluctuations that can impact both comfort and equipment.
- Reduced Noise: Advanced systems operate more quietly than older models, contributing to a peaceful environment.
- Automation and Convenience: Integration with smart home technologies allows for remote control and scheduling, adding convenience and efficiency.
- Humidity Regulation: Controls indoor humidity levels to prevent issues like mold growth and damage to building materials.
- Long-Term Cost Savings: Properly maintained systems can extend the lifespan of HVAC equipment, reducing the frequency of replacements and repairs.
Types of HVAC Systems
HVAC systems are essential for maintaining indoor comfort, and they come in various types suited to different building needs. These systems are broadly categorized into two main configurations: ducted and ductless, each offering distinct features and benefits.
Ducted HVAC Systems
Ducted HVAC systems use a network of ducts to distribute air throughout a building. This category includes the following types:
Split System: A split system is a popular choice for residential buildings, consisting of an indoor unit (such as a furnace or heat pump) and an outdoor unit (air conditioner). This configuration allows for efficient heating and cooling of the entire home, managed by a single thermostat. Known for its reliability and effectiveness, the split system provides consistent indoor climate control throughout the year.
Hybrid Split System: The hybrid split system combines a heat pump with a furnace, offering a versatile solution that utilizes both gas and electric power. This dual-fuel capability allows homeowners to optimize energy usage based on prevailing weather conditions. Particularly beneficial in milder climates, the hybrid system can switch between fuel sources to reduce energy consumption and operational costs while maintaining a comfortable indoor environment.
Packaged Heating and Cooling: Packaged heating and cooling systems house all components in a single unit, making them ideal for small buildings with limited space. Typically installed on rooftops or near the building’s foundation, their compact design simplifies installation and maintenance. Packaged units are cost-effective and provide a practical solution for buildings requiring straightforward and efficient HVAC systems.
Zoned System: Zoned HVAC systems offer personalized comfort by dividing a building into different zones, each with its own thermostat and set of dampers within the ductwork. This setup allows for independent temperature control in various areas of a building, making it suitable for large residential homes or commercial spaces. Zoned systems enhance energy efficiency by only heating or cooling occupied zones, thus reducing energy waste and improving overall comfort.
Ductless HVAC Systems
Ductless HVAC systems do not use ducts to distribute air. Instead, they deliver air directly to specific zones or areas. This category includes the following types:
Duct-Free Mini-Split: Duct-free mini-split systems consist of an outdoor compressor and one or more indoor air-handling units. These systems are perfect for multifamily homes, office buildings, and hotels where ductwork is impractical or non-existent. Mini-splits offer independent temperature control for different zones, which is particularly useful for buildings with diverse heating and cooling needs. Although initially more expensive, they significantly reduce energy costs and consumption over time, especially in spaces where traditional ducted systems are not feasible.
Hydronic Heating: Hydronic heating systems use water heated by a boiler, which is then distributed through pipes to radiators or radiant floor systems. This method of heating provides consistent and comfortable warmth. Hydronic systems are highly efficient and often used in residential and commercial buildings with radiant floor heating. The use of liquid to radiate heat ensures even distribution and maintains a pleasant indoor environment, particularly in colder climates.
Portable Units: Portable HVAC units, including portable air conditioners and heat pumps, offer flexible solutions for temporary or supplementary heating and cooling needs. These units are ideal for temporary construction sites, small spaces, or areas requiring spot cooling or heating. Easy to transport and install, portable units provide a convenient way to manage indoor climate on an as-needed basis. Their versatility makes them suitable for various applications, ensuring comfort can be maintained even in challenging or transient environments.

Applications of HVAC Systems’
- Residential Buildings
- Commercial Buildings
- Industrial Facilities
- Healthcare Facilities
- Educational Institutions
- Hospitality Industry
- Retail Spaces
- Data Centers
- Public Buildings
- Transportation Hubs etc.
Market Potential of HVAC System in India
As per the TechSci Research report, the India HVAC Market reached USD 9.1 billion in 2023, projecting a CAGR of 14.5% during the forecast period of 2025-2029. The Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) industry in India has experienced notable growth and transformation due to rapid urbanization, rising incomes, and increased awareness of indoor air quality.
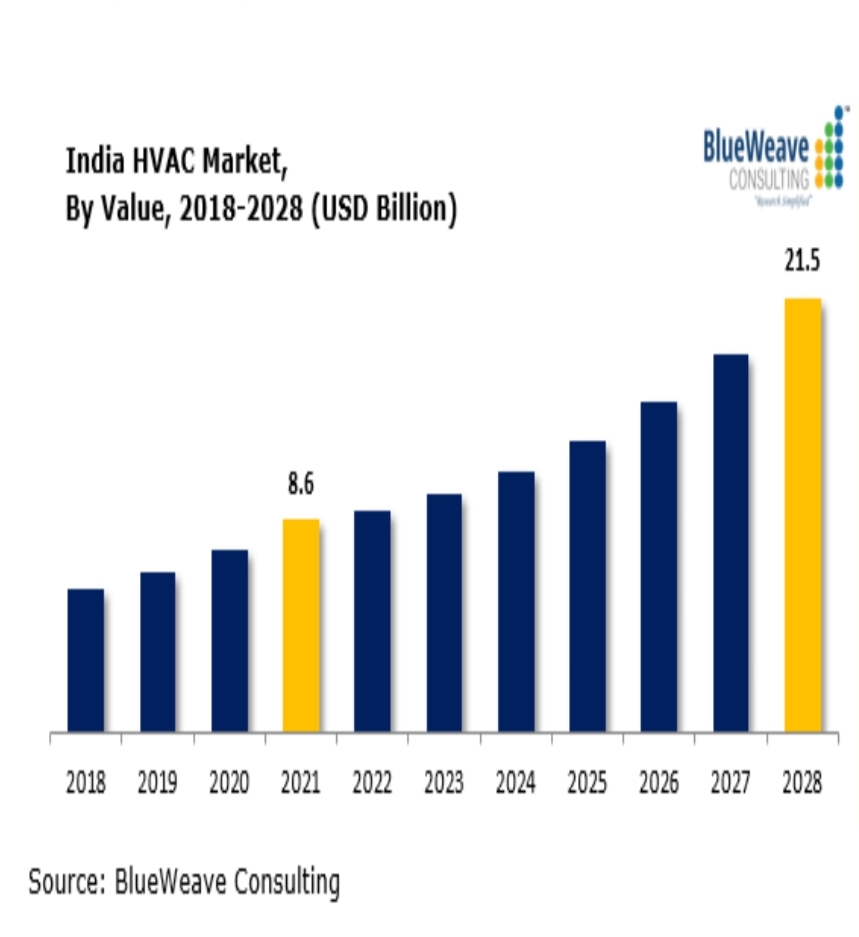
As per BlueWeave Consulting report, India HVAC market was worth USD 8.6 billion in 2021 and is further projected to reach USD 21.5 billion by the year 2028, growing at a CAGR of 14.80% in the forecast period. The market is growing at a high rate owing to factors such as rising disposable income and purchasing power of the consumers along with increasing investment towards infrastructural development and construction of various residential and commercial facilities. Furthermore, the integration of advanced technologies such as IoT is also offering significant growth opportunities to the India HVAC market.
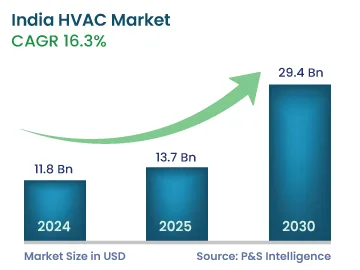
As per PS Market Research report, the Indian HVAC market size is estimated to be around USD 11.8 billion in 2024, and it is projected to reach USD 29.4 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 16.3%. between 2024 and 20230. This growth is attributed to infrastructure developments and technological advancements within the country.
Conclusion
HVAC systems are pivotal in maintaining optimal indoor environments across various settings by effectively regulating temperature, humidity, and air quality. As essential components of modern buildings, these systems enhance comfort, energy efficiency, and overall well-being. With advances in technology, including smart controls and energy-efficient designs, HVAC systems continue to evolve, offering improved performance and sustainability. As global demands and environmental standards shift, the HVAC industry must adapt, embracing innovations that address both user needs and ecological impacts. Understanding the fundamentals and types of HVAC systems empowers stakeholders to make informed decisions, ensuring that their choices align with both operational goals and long-term benefits.
Image sources- perthairandpowersolutions, icominc.com/hvac-system, parametric-architecture.com








.png)